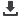
Fig.
3.
CT
scans
showing
an
erosion
of
the
ethmoidal
roof
((A)
SE,
(B)
EE)
or
of
the
posterior wall
of
the
frontal
bone
(*)
((C)
EE).
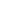
Fig. 4.
Cerebral
imaging at
the
time of maximal extension of empyema
(*). These
images show
that SE
is usually
larger
than EE,
reaches areas situated way above
the ethmoid and
frontal
sinuses
and,
also
often
extends
to
the
interhemispheric
region. While
EE
shows
typical
biconvex
contours,
SE
has
a more
irregular
shape,
sometimes
displaying
a
multilocular
appearance
(A3,
A4,
A5, A6,
A7,
and
A9).
A.
Garin
et al.
/
International
Journal
of
Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology
79
(2015)
1752–1760
89