between the level of anesthesia groups. This method was
used to account for the dependency of FNAB across
encounters within patients.
17
The 2015 Standards for
Reporting of Diagnostic Accuracy (STARD) guideline for
reporting diagnostic accuracy studies was used.
18
Results
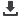
Over the 7-year study period, 257 patients who underwent
at least 1 FNAB were identified. By having multiple
FNABs at 1 or multiple visits, there were 338 total FNABs,
with 284 specific encounters (
Figure 1
). Baseline charac-
teristics of the patients are shown in
Table 1
. The 169
patients in the nonthyroid group were younger (mean age,
7.1 vs 13.6 years,
P
\
.001) and had a lower percentage of
females (38.5% vs 77.3%,
P
\
.001) than the 88 patients in
the thyroid group. The mean (SD) size of the 189 masses
with prebiopsy imaging was 2.4 (1.73) cm (range, 0.3-12.5
cm). The average time between FNAB and surgery was 73
days (range, 0-1183 days). The volume of FNABs per-
formed per month steadily increased from 3.2 in 2007 to 7.2
in 2014 with no seasonal variation.
Diagnostic Accuracy
The overall pathologically confirmed sensitivity and specifi-
city were 93.5% and 64.3%, respectively (
Table 2
). If clini-
cally and pathologically confirmed results are combined,
sensitivity was 94.6% and specificity was 97.7% (
Table 2
).
When rapid on-site interpretation yielded a preliminary
diagnosis, it correlated with final cytopathology 99.1% of
the time (n = 106) and final surgical histopathology 93.3%
of the time (n = 30). The false positives and false negatives
are presented in
Table 3
.
The clinical nonthyroid HNM sensitivity and specificity
were 98.2% and 97.7%, respectively, representing 190 total
FNABs (
Table 2
). There were an additional 20 nondiagnos-
tic specimens (9.5%).
Table 4
presents the final diagnoses,
the most common of which was benign reactive lymphade-
nopathy (BLN), present in 99 patients. Malignancy was
detected in 6 of the 169 patients (3.6%), including a meta-
static medullary thyroid carcinoma that was not confirmed
by thyroid FNAB prior to thyroidectomy.
There were 118 thyroid FNABs, with a clinical sensitiv-
ity of 88.6% and specificity of 97.6% (
Table 2
). There
were 10 nondiagnostic results (7.8%). The most common
diagnosis was benign colloid nodule, found in 31 children.
Fifteen malignancies were detected in the 88 patients under-
going thyroid FNABs (17.0%), most commonly papillary
thyroid carcinoma. The rates of malignancy by are pre-
sented TBSRTC
4
category in
Table 5
with comparisons to
a large pediatric thyroid FNAB series.
19
The overall FNAB nondiagnostic rate was 8.9% (n = 30).
All 10 of the thyroid nondiagnostic results were performed
with image guidance and under general anesthesia (GA) or
sedation. Of the 20 nonthyroid nondiagnostic results, there
PotenƟally eligible parƟcipants (n = 257)
Eligible parƟcipants (n = 257)
Excluded (n = 0)
No FNAB (n = 0)
Non-thyroid FNAB
posiƟve (n = 57)
Non-thyroid FNAB
negaƟve (n = 133)
Non-thyroid FNAB
non-diagnosƟc
(n = 20)
Thyroid FNAB
posiƟve (n = 35)
Thyroid FNAB
negaƟve (n = 83)
Thyroid FNAB non-
diagnosƟc (n = 10)
FNAB (n = 338)
Histopathology (n = 43)
Histopathology (n = 8)
Histopathology (n = 34)
Histopathology (n = 6)
Histopathology (n = 5)
Histopathology (n = 1)
HP posiƟve: 40
HP negaƟve: 3
HP posiƟve: 1
HP negaƟve: 7
HP posiƟve: 2
HP negaƟve: 4
HP posiƟve: 32
HP negaƟve: 2
HP posiƟve: 4
HP negaƟve: 2
HP posiƟve: 0
HP negaƟve: 1
No Histopathology (n = 1)
Lymphoma (n = 1)
No Histopathology (n = 14)
ATB (n = 8)
LVM (n = 4)
Neck abscess (n =2)
Figure 1.
STARD flowchart of enrolled patients and FNAB. ATB, atypical tuberculosis; FNAB, fine-needle aspiration biopsy; HP, histo-
pathology; LVM, lymphovenous malformation.
Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery 154(5)
192