The overall sensitivity and specificity of the thyroid
FNAB was 88.6% and 97.6%, respectively, which is consis-
tent with reports within both the general and pediatric popu-
lations.
19,28-30
The applicability of The Bethesda System
(TBSRTC) to the pediatric population has been previously
examined in the literature and is a recommendation of the
2015 American Thyroid Association (ATA) Guidelines for
Pediatric Thyroid Nodules and Cancer.
6,19
We found the 128
thyroid FNABs to have excellent concordance with the rates
of malignancy as described by TBSRTC
4
(
Table 5
). Similar
to Lale et al,
19
there was an increased rate of malignancies in
the indeterminate TBSRTC categories (III, IV, and V).
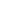
Table 3.
False-Positive and False-Negative FNAB with Final Histopathologic Result, Explanation of Error, and/or Patient Outcome.
Error
FNAB
Histopathology
Outcome
False negative
BCN (
3
2)
Encapsulated follicular PTC
Sampling error (6.8 cm)
31
; surgery
without delay, no complications
False negative
BCN
Follicular adenoma
1
papillary
hyperplasia
Resolved with surgery, no
complications
False negative
BLN
Hyaline variant of
Castleman’s disease
39 months between initial
FNAB and surgery; resolved with
surgery, no complications
False negative
Suspicious for PTC
FTC
Both are TBSRTC suspicious for
malignancy
4
; surgery
without delay, no complications
False positive
Suspicious for PTC
Nodular hyperplasia
with 2 dominant nodules
Resolved with surgery, no
complications
False positive
Heterogeneous lymphoid
population with atypia
BLN
Resolved with surgery, no
complications
False positive
Suspicious for
lymphoproliferative disorder
Reactive primary
follicular hyperplasia
Resolved with surgery, no
complications
False positive
Follicular lesion or neoplasm Hyperplastic colloid nodule
70%-85% of SFONs are
expected to be benign
4
; resolved
with surgery, no complications
False positive
Low-grade mucoepidermoid
carcinoma
Kuttner tumor
Resolved with surgery, no
complications
Abbreviations: BCN, benign colloid nodule; BLN, benign lymphadenopathy; FNAB, fine-needle aspiration biopsy; FTC, follicular thyroid carcinoma; PTC, papil-
lary thyroid carcinoma; SFON, follicular neoplasm or suspicious for follicular neoplasm; TBSRTC, The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology.
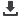
Table 2.
Sensitivity, Specificity, and Positive and Negative Predictive Values.
Characteristic
HP
1
, No.
HP–, No.
PPV/NPV, % Sensitivity/Specificity, %
All, histopathologically proven only
93.5/64.3
93.5/64.3
FNAB positive
72
5
FNAB negative
5
9
Characteristic
HP and Clinically
Positive, No.
HP and Clinically
Negative, No.
PPV/NPV,
%
Sensitivity/
Specificity, %
All, histopathological plus clinical follow-up
94.6/97.7
94.6/97.7
FNAB positive
87
5
FNAB negative
5
211
Nonthyroid
94.9/99.2
98.2/97.7
FNAB positive
56
3
FNAB negative
1
130
Thyroid
93.9/95.3
88.6/97.6
FNAB positive
31
2
FNAB negative
4
81
Abbreviations: FNAB, fine-needle aspiration biopsy; HP, histopathologically; NPV, negative predictive value; PPV, positive predictive value.
Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery 154(5)
194