42
Controlling and limiting the road transport and intake to mills
provides one of the primary opportunities for limiting the total
amount of logging from regions with high rates of illegal log-
ging. Introducing road or timber taxes also makes illegal tim-
ber less attractive from such areas. However, imposing such a
tax would have to provide rewards, bounties or returns for local
officers that are greater than the typical bribe paid per truck in
order to be an effective incentive to enforce. Hence, identifying
the level of tax or tariff to be imposed will depend upon the
region, the rate of illegal logging, its value, and the bribes com-
monly paid in the region.
Controlling the bottlenecks, combined with road or transporta-
tion tariffs dependent upon rate of deforestation and criminal
activity in the region would raise the cost of illegal timber to the
same cost as legal timber. This would also increase the costs for
mills processing illegal wood and impact their attractiveness on
the stock markets for investors.
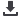
Illegal logging bottlenecks
>
>
>
>
Wood is illegally
logged and collected
Wood is transported
to mills with trucks
Wood is transported
by river
Border crossing
Timber aggregation point
Border crossing point
Harbour for international shipping
Source: Personal communication with Christian Nellemann.
Mill or other wood processing facility
Bottlenecks
Mills and processing
facilities far from the
logging area pay more in
transportation costs