CONTROL SYSTEMS + AUTOMATION
semiconductor components has fallen sharply over recent years,
whilst battery technology has steadily improved. These phenomena
can be largely attributed to the mass adoption of smart phones, re-
sulting in aggressive international competition and accelerated R&D
cycles. The reduction in price, coupled with higher integration of core
components and extended battery life, is quickly opening up new
opportunities for connected devices. In order to effectively address
this rapidly growing market, it is clear that a new communication
platform is required.
Much like the collaboration between telecommunication leaders
in the 80s to establish GSM, there has been large-scale industry col-
laboration to create LPWA standards, especially over the past three
years. This has resulted in the establishment of several reliable, secure
and commercially viable LPWA network platforms.
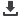
Figure 3: LPWA networks address the need for ubiquitous long range,
low-power communication.
Open Access LoRaWAN network – a game changer
Comsol Networks has selected LoRa as the technology behind their
LPWA network. The company has embarked on the largest roll-out
of a LoRa Wide-Area Network (LoRaWAN) in Africa to date, aiming to
cover four major metropolitan areas in Q1 2017, with more to follow.
This company is not alone. National LoRa networks have already be
deployed, or are being deployed in countries around the world. No-
table examples are South Korea, Holland, France and the US, but the
list is virtually endless. LoRaWAN will not be the only LPWA network
technology available in South Africa, but it offers a unique set of fea-
tures that set it apart from other options. The protocol was developed
by global network and radio communication leaders in the form of
IBM and Semtech respectively. LoRaWAN is a fully documented
open protocol, which is overseen and managed by an international
consortium known as the LoRa Alliance
(www.lora-alliance.org).
Membership to the alliance is open to any organisation, and today
the alliance boasts more than 400 members worldwide, including
some of the largest brands in the technology sector.
The LoRa modulation scheme uses advanced spread-spectrum
techniques and forward error correction to minimise susceptibility to
co-channel interference, allowing the receiver to decode signal levels
well below the ambient noise floor. The Adaptive Data Rate (ADR)
feature of the network dynamically adjusts the communication data
rate (293 bps up to 5 kbps) of devices based on the received SNR,
reducing unnecessary time-on-air, and resulting in longer battery life
and greater network capacity. The bi-directionality of the LoRaWAN
network allows for wireless actuation of devices in the field, as well
as the remote updating of settings, or targeted bug fixes. Comsol’s
LoRa network operates within the 868 MHz licence-free spectrum,
offering good range and penetration, whilst keeping antenna sizes
within practical limits.
All transmissions within the network are secured via 128-bit AES
encryption on both the network and application layers. Payload data
received by the network is translated and presented to the user’s
application layer via a secure TCP/IP socket, in a variety of easily us-
Electricity+Control
February ‘17
12