C a r d i o v a s c u l a r D i s o r d e r s
Chapter 6
• Cardiovascular Disorders
67
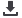
Right-sided heart failure
Ineffective right ventricular contractility
Failure of right ventricular pumping ability
Decreased cardiac output to lungs
Blood backup into right atrium and peripheral circulation
Weight gain, peripheral edema, engorgement of liver and other organs
Left-sided heart failure
Ineffective left ventricular contractility
Failure of left ventricular pumping ability
Decreased cardiac output to body
Blood backup into left atrium and lungs
Pulmonary congestion, dyspnea, activity intolerance
Pulmonary edema and right-sided heart failure
TYPES OF HEART FAILURE
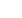
Pulmonary arteries
Pulmonary veins
Left atrium
Left ventricle
Superior vena cava
Pulmonary arteries
Pulmonary veins
Right atrium
Right ventricle
Inferior vena cava
NORMAL CARDIAC CIRCULATION
•
Radionuclide ventriculography reveals an ejection fraction
less than 40%; in diastolic dysfunction, the ejection fraction
may be normal.
Treatment
•
Treatment of the underlying cause, if known
•
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or ARBs (for
patients with left ventricular dysfunction), specific beta-adrenergic blockers (for patients with left ventricular dysfunc-
tion), diuretics, digoxin, nitrates, morphine, or oxygen
•
Dobutamine, milrinone, and nesiritide (for refractory HF)
•
Lifestyle modifications to reduce risk factors
•
Coronary artery bypass surgery (if caused by CAD), angio-
plasty, or heart transplantation
•
Placement of prophylactic ICD (with or without Bivent
pacing) for patients with low EF