Silliker
Chem, Res. Center Crete, IL – Report of A Validation of LC-MS/MS Method for Folate Analys
9
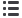
Time (min)
%B
Flow
(mL/min)
0
0
0.5
0.5
0
0.5
5.00
40
0.5
5.05
100
0.5
6.50
100
0.5
6.55
0
0.5
9.00
0
0.5
A = 1%Acetic Acid in Water
B = 100% Methanol
Column Temperature: 40
r
C
Autosampler Temperature: 6
r
C
Injection Solvent: Std., samples and blanks injection solvent is 90% MeOH + 10% Formic acid +
1% ascorbic acid neutralized to pH 7 with ammonium hydroxide (29%), 50 uL/mL.
Injection Volume = 2 uL
Investigation of different Injection Solvents Chromatography obtained by the method:
Various solvent mixture were evaluated for their effect on chromatography and resolution of the
analytes. The most important solvent mixture tried are mixtures A and G and are listed in the following
section. The solvent A is used for elution of the analytes during solid-phase extraction. We tried a step
of the evaporation of the extract concentrated and purified by SPE to improve sensitivity of the method.
The extract residue following the evaporation is reconstituted in the following solvent mixture G which
is some what similar to the HPLC mobile phase used in the analysis.
A: 90% MeOH + 10% Formic acid + 1% ascorbic acid
G: 20% methanol + 80% of 1% acetic acid + 1% ascorbic acid
A standard mixture was taken in either solvent mixture A or the solvent mixture G and analyzed by the
chromatographic and MS method described above. A representative chromatogram of the analytes in
two different injection solvents is provided in the following Figure 1. The analytes could be
satisfactorily resolved by the chromatography and the injection solvent did not have any considerable
effect. Injection solvent A was used in the remaining part of the study.
2011.06/Fol-22 (February 2016)
FOR ERP USE ONLY
DO NOT DISTRIBUTE