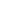
Table 1: Expected Functionality of Independent Protection Layers
Layer of Protection Expected Functionality
BPCS:
Keeping the process under control
Alarms:
Alerting the operator of abnormal conditions
and providing guidelines for appropriate
operator response
SIS:
Automatically taking the process to a safe
condition in case the abnormal condition
goes out of control and the operators can’t
take any corrective action in time
Other layers:
Intended to mitigate the consequence of the
hazard
The concept of Independent protection layers (IPL) can also be illustrated in Figure 1
3. Common Cause Failures
The idea of functional independent systems is an attempt to avoid Common Cause Failures (CCF).
Common Cause Failures [3] are failures that might affect more than one of these protection layers at the same
time. As engineers, the tendency will be to focus on elements such as Heat, Humidity, Shock, and radio
interference among others. However this paper also considers, with special interest, the human elements
related to the design of safety critical systems which can contribute to additional failures.
As with other systems, some SIS problems are related to the Commercial Off the Shelf (COTS) products
designed for a specific function (i.e. hardware limitations or poor documentation) while other problems are
related to the use of those COTS product such as misapplication, user application programming or poor
maintenance practices. Both areas can be addressed by implementing appropriate design best practices to
reduce risk.