ENVIRONMENT REPORT
2015
page 28
3.6 Waste
In any discussion on waste, it is important to understand the meaning of waste given the various definitions
and interpretations that exist. According to the EU Waste Framework Directive (2008/98/EC) waste “means any
substance or object which the holder discards or intends or is required to discard.” As with the creation of any
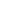
product, oil and gas production is associated with waste generation and disposal. As illustrated in Figure 16,
waste originates at various points in the oil and gas life cycle and can be in different states, including solid, liquid,
hazardous and non-hazardous (inert) materials.
Figure 16: Waste Generated Offshore by Waste Source
Waste infographic
Decommissioning
General Waste
Food Waste
Special Waste
Clinical Waste
General Waste
Food Waste
Special Waste
Clinical Waste
Scrap Metal
Explosives
Asbestos
To shore
Deco missioning
General Waste
Food Waste
Special Waste
Clinical Waste
Scrap Metal
*
*
*
* General waste can include empty containers, segregated recyclables and liquid wastes. Special waste includes similar
materials to general waste, however, these materials are generally classified as hazardous.