58
Source: Vanat, L. (2016) 2016 International
Report on Snow & Mountain Tourism – Overview of
the key industry figures for ski resorts. 8th edition.
*
Ski station located in Israeli-occupied Syrian territory.
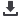
Number of Ski Stations:
Less than 10
Between 10 and 100
More than 100
Number of
skier visits
per year
30 000 000
10 000 000
3 000 000
1 000 000
300 000
European and North American countries
CHILE
ARGENTINA
SOUTH AFRICA LESOTHO
MOROCCO
TURKEY
ISRAEL*
JAPAN
CHINA
INDIA
PAKISTAN
IRAN
RUSSIA
KAZAKHSTAN
AZERBAIJAN
ARMENIA
GEORGIA
LEBANON
KYRGYZSTAN
UZBEKISTAN
TAJIKISTAN
MONGOLIA
AUSTRALIA NEW ZEALAND
SKI STATIONS OUTSIDE OF EUROPE & NORTH AMERICA, 2016
• Littering by skiers on the slopes: organic and non/organic
waste is thrown along ski runs or from lifts simply because
there is no waste disposal nearby (NSAA, 2005). Littering
depends to a certain extent on cultural norms and practices,
which can differ from region to region.
• Waste generated by ski resorts and villages, which includes the
whole spectrum of organic and non-organic waste.
• The physical infrastructure in ski resorts: the construction of
access roads, ski slopes and ski lifts carry with it environmental
implications: deforestation, disturbance to wildlife, soil erosion
and habitat fragmentation (Rixen and Rolando, 2013). The
construction of hotels and buildings result in large amounts of
construction waste.
• The environmental implications of artificial snow: climate change
is a big threat to the ski industry because it is expected to bring
warmer winters, reduced snowfall and shorter seasons (for
example, Dawson & Scott, 2013; Agrawala, 2007). One solution
is the use of snow cannons to create artificial snow. This practice
can cause changes in vegetation (Gilaberte-Búrdalo et al., 2014)
and uses significant amounts of energy and water, which is often
Ski tourism, winter Olympics and waste
implications
Ski tourism is a winter activity attracting large numbers of tourists
to Europe (particularly the Alps) andNorth America. Ski resorts also
exist in other mountainous regions in Central and South Asia, the
Caucasus, theMiddle East, South America and China. Many regions
are currently developing or expanding their ski industry. China, in
particular, has seen a dramatic growth in the number of ski resorts
as well as improvements in their quality (Vanat, 2016).
Skiing is often developed for mass tourism, which brings with it
numerous waste challenges ranging from littering on the slopes,
waste produced by ski resorts, to waste implications related to
building and maintaining the physical infrastructure on the
slopes and in resorts.
The literature on the impacts of ski tourismon the environment, and
the waste implications and solutions, is largely limited to examples
from the European Alps and North America. These include: