10
MODERN MINING
June 2015
MINING News
Leading explosives supplier BME has
raised the bar with a record blast at
Zambia’s Kansanshi mine in March 2015,
detonating 4 141 electronic delay deto-
nators (EDDs) in a single blast in the
operation’s north-west pit.
“This is a great achievement for the BME
team in Zambia and another milestone
for the AXXIS system,” said BME’s Country
Manager in Zambia, Charles Pretorius. “It
is our second record for the most EDDs in
one blast for BME world-wide, beating our
own record of last year.”
Wayde de Bruin, the Senior Operations
Manager on site, said the blast comprised
a main block, as well as trim just above the
main block. The blast was done using one
master blasting box at the point of blast-
ing communicating remotely to the slave
boxes and detonators down in the pit.
To improve the safety, ease of use and
accuracy of blasts, BME developed AXXIS –
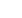
The north-west pit at Kansanshi showing the area of the record-breaking blast (photo: BME).
Another BME blasting record in Zambia
its own digital initiation system. The system
allocates precise firing times to detonators,
allowing engineers to design complex
firing sequences in a blast to achieve desir-
able and repeatable blast results.
“Everything went according to plan,
with the logging, programming, status
check and the blast itself all on schedule
and with good results,” said de Bruin. “We
are now only 645 detonators away from
the overall African record.”
BME has been a pioneering force in
the field of electronic detonation, which is
growing in popularity as more mines and
quarries benefit from the reliability and
accuracy of these devices.
According to BME Technical Director
Tony Rorke, the accuracy of electronic deto-
nators is not only making blasting practice
more predictable, but is also allowing for
larger and more cost-effective blasts. Now
the leading supplier of explosives to the
South African open-pit mining and quar-
rying industry, BME is also an innovator of
various blast-related services and products.
“The use of shocktube (non-electric)
detonators has always had the limitation of
being reliant on hard-wiring throughout,”
said Rorke. “This places certain constraints
on the blast design and implementation,
and can raise the risk of a mis-fire under
certain conditions.”
The advantages of using electronic det-
onators include the ability to trigger blasts
through a wireless signal. Included in these
are that blasting lines to the detonators are
less likely to be damaged, thereby substan-
tially reducing the likelihood of a mis-fire.
Blanket mine upgrades its resource base
Canada’s Caledonia Mining has announced
an increase and upgrade to the resource
base at its 49 %-owned subsidiary, the
Blanket mine in Zimbabwe.
Based on the drilling that has been com-
pleted at depth below the AR Main and
Blanket sections over the past year, it has
been possible to upgrade 491 000 tonnes
from the inferred to the indicated resource
category and to add 47 000 tonnes of new
inventory to indicated resource.
This upgraded indicated resource of
538 000 tonnes is additional to the 2,93 Mt
of reserves and indicated resource that was
used for the Reserve Plan in the Technical
Report prepared by Minxcon in December
2014 and represents an increase of 17,4 %
in terms of tonnes and 20,5 % in terms of
contained gold.
Commenting on the resource upgrade,
Steve Curtis, Caledonia’s Chief Executive
Officer, said: “This upgrade reflects an
increased focus on resource development
at the Blanket mine. The rate of explora-
tion drilling has increased and will increase
further when the new drill machines, which
have already been ordered, are delivered
and commissioned.
“The upgrade of approximately 491 000
tonnes from inferred resource to indicated
resource represents a significant improve-
ment in the overall confidence level of
Blanket’s resources.”
When the Preliminar y Economic
Assessment was completed in late 2014
for the revised investment plan at Blanket
mine, approximately 55 per cent of Blanket’s
resource base comprised measured and
indicated resources and 45 per cent com-
prised inferred resources.
After the upgrade, the resources split
has improved to 62 % in the measured and
indicated category and 38 % in the inferred
category.