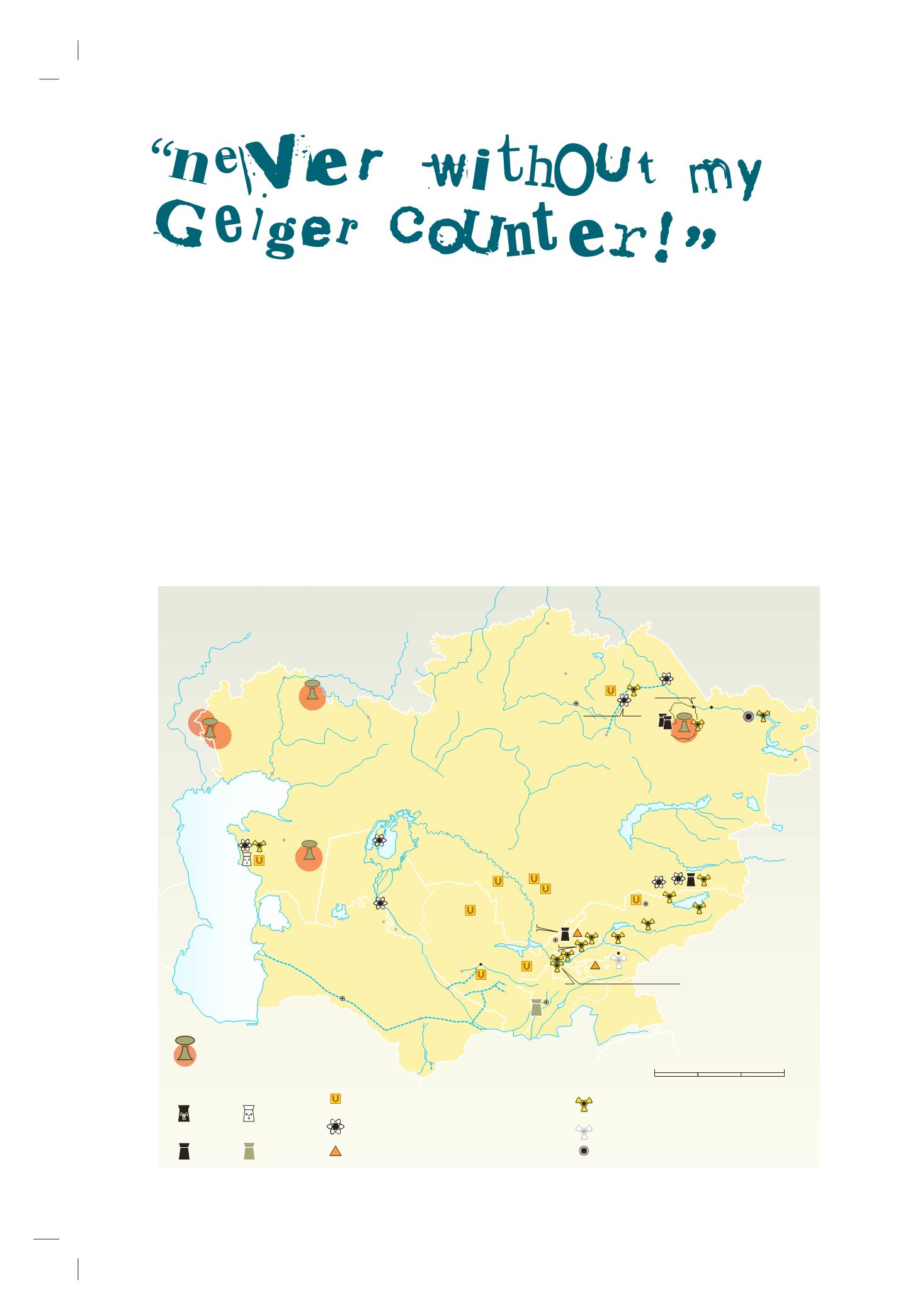
Thus jokes Oleg, the leader of an NGO in Central Asia when
he plans field trips through the region. In fact, this is almost
not a joke considering that the area is home to many radio-
active dumps. This specific type of waste, inherited from
the Soviet era, poses serious management problem, recog-
nized both by governments and international organizations.
For example, around the Fergana Valley, in a region prone
to landslides, radioactive tailing ponds have the potential
to flow into rivers and contaminate the drinking water of
millions of people. Radioactive waste exits in many other
areas – dumped in the Barents Sea, or simply abandoned in
forests and fields all over the territory of Georgia.
What is radioactive waste?
Radioactive waste is any material that
contains a concentration of radionuclides
greater than those deemed safe by na-
tional authorities, and for which no use is
foreseen. Because of the wide variety of
nuclear applications, the amounts, types
and even physical forms of radioactive
waste vary considerably – some waste
remain radioactive for hundreds or thou-
sands of years, while others may require
storage for only a short period, while they
decay, prior to conventional disposal. (In-
ternational Atomic Energy Agency).
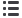
RADIOACTIVE WASTE
Bishkek
Tashkent
Zaisan
Semey
(Semipalatinsk)
Karagandy
Astana
Kiziliar
(Petropavlosk)
Atyrau
Oral
Aktobe
Kustanau
Makinsk
Dushanbe
Ashgabad
Kzyl-Orda
Tyuratam
UST-
KAMENOGORSK
Bukhara
Turkmenbashi
Mary
Turkmenabad
Dashoguz Urgench
Osh
Navoy
KARAKALPAKSTAN
AZGYR
LIRA
(Burlinskiy)
SAY-UTES
TEST SITE
Say-Utes
SEMIPALATINSK-
KURCHATOV
TEST SITE
Kurchatov
MINING
DIRECTORATE
No. 6
STEPNOYE
TSENTRALNOYE
UCH-KUDUC
ZAFARABAD
NURABAD
AK-TUZ
KARA-
BALTA
KADZHI-SAY
MAILU-SUU
MIN-KUSH
KHAIDARKAN
SHEKAFTAR
TEREK-SAY
TEO-MOYUN
VOSTOKREDMET (CHKALOVSK)
AND TABOSHAR
CHARKASSAR
AKTAU
MANGYSHLAK
ATOMIC ENERGY
COMBINE (MAEK)
ALATAU
INSTITUTE OF
NUCLEAR PHYSICS
KAZSABTON
(former Tselinny
Mining and
Chemical Combine)
KASKOR JSC
(former Prikaspiyskiy
Mining and Metallurgy
Combine)
ULUGBEK
VOZROZHDENIJE
PENINSULA
NUKUS
STEPNOGORSK
PAVLODAR
OTAR ALMATY
KASPUTIN YAR
FERGHANA
(Closed)
CASPIAN
SEA
ARAL
SEA
LAKE
BALKHASH
Volga
A
m
u
-
D
a
r
i
a
S
y
r
-
D
a
ri
a
I
s
h
y
m
T
o
b
o
l
U
r
a
l
I
r
t
y
s
h
KYRGYZSTAN
KAZAKHSTAN
UZBEKISTAN
TAJIKISTAN
IRAN
AFGHANISTAN
TURKMENISTAN
CHINA
AZERBAIJAN
RUSSIA
PAKISTAN
RUSSIA
200
400
0
600 km
Radioactive, chemical and biological
waste in Central Asia
R
R
Former nuclear test site
with possible remaining
radioactive wastes
Uranium mining and milling facility. Radioactive
waste related to exploitation
Radioactive waste storage site generally poorly
maintained, and alleged to pose a significant risk
to health and environment
Nuclear power plant
Active
Power reactor
Closed
Research reactor
Active
Closed
Fuel production
Chemical and biological research center or
production plants being dismantled
Old radioactive waste site (early 20th century)
Non-radioactive waste site (mercury, antimony)
R
R
R
R
R