F. Calculations
The vitamin D
3
standard linear curve with a 1/x weighting is calculated using the total
area of the vitamin D
3
and the previtamin D
3
(if present) with the total area of the isotope
vitamin D
3
and the isotope previtamin D
3
as the internal standard. The sample vitamin
D
3
concentration is calculated from the above curve using the sample total area of the
isotope vitamin D
3
and the isotope previtamin D
3
as the sample internal standard. The
sample previtamin D
3
concentration is calculated from the same curve and the same total
area of the isotope vitamin D
3
and the isotope previtamin D
3
as the sample internal
standard.
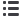
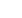
IU/100g
100
)
FCIS(IU/mL
weight(g)
)
CISS(IU/mL
ISS(mL)
/mL)]
SCPreD3(IU
U/mL)
[SCVitD3(I
= ×
×
×
×
+
Where:
SCVitD3 = sample concentration vitamin D
3
, IU/mL, from linear curve;
SCPreD3 = sample concentration previtamin D
3
, IU/mL, from linear curve;
ISS = amount of internal standard spiked in sample, mL;
CISS = concentration of internal standard spiked in sample, IU/mL;
weight = sample size taken, g;
FCIS = final concentration of internal standard in working standards, IU/mL. Vitamin
D
2
is calculated in the same way.
Note:
•
Respective qualifying product ions should match the quantitation ions within 20%
to confirm the presence of vitamin D
2
or D
3
. The quantitation ion for vitamin D
3
is 385.4/259.1 while the qualifier ions for vitamin D
3
are 385.4/107.1 and
385.4/159.1. For vitamin D
2
the quantitation ion is 397.4/125.1 while the
qualifier ions are 397.4/107.0 and 397.4/271.1.
•
1 mcg vitamin D = 40 IU
•
All steps of the method procedure should be conducted in low actinic light
2011.11 VITAMIN D MLT-Sept 2015
FOR ERP USE ONLY
DO NOT DISTRIBUTE