City of Morgan Hill
Sanitary Sewer Flow Monitoring and Inflow/Infiltration Study
12-0248 AEG CofMorganHill FM Rpt.docx
Page 27 of 46
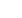
Figure 19. Inflow and Infiltration: Graphical Response Patterns
Infiltration Components
Infiltration can be further subdivided into components as follows:
Groundwater Infiltration:
Groundwater infiltration depends on the depth of the groundwater
table above the pipelines as well as the percentage of the system submerged. The variation
of groundwater levels and subsequent groundwater infiltration rates is seasonal by nature.
On a day-to-day basis, groundwater infiltration rates are relatively steady and will not
fluctuate greatly.
Rainfall-Dependent Infiltration:
This component occurs as a result of storm water and
enters the sewer system through pipe defects, as with groundwater infiltration. The storm
water first percolates directly into the soil and then migrates to an infiltration point. Typically,
the time of concentration for rainfall-related infiltration may be 24 hours or longer, but this
depends on the soil permeability and saturation levels.
Rainfall-Responsive Infiltration
is storm water which enters the collection system indirectly
through pipe defects, but normally in sewers constructed close to the ground surface such as
private laterals. Rainfall-responsive infiltration is independent of the groundwater table and
reaches defective sewers via the pipe trench in which the sewer is constructed, particularly if
the pipe is placed in impermeable soil and bedded and backfilled with a granular material. In
this case, the pipe trench serves as a conduit similar to a French drain, conveying storm
drainage to defective joints and other openings in the system. This type of infiltration can
have a quick response and graphically can look very similar to inflow.
0.00
0.10
0.20
0.30
0.40
0.50
0.60
0.70
0.80
0.90
1.00
Flow (MGD)
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
Rain (in/hr)
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
0.30
0.35
0.40
0.45
0.50
4-Jun
5-Jun
I/I (MGD)
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
Rain (in/hr)
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
Flow (gpm)
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
Rain (in/hr)
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
22-Feb
23-Feb
Flow (gpm)
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
Rain (in/hr)
0.00
0.10
0.20
0.30
0.40
0.50
Flow (MGD)
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
Rain (in/hr)
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
17-Dec
18-Dec
19-Dec
20-Dec
Flow (MGD)
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
Rain (in/hr)
Inflow
Combination I/I
Infiltration
Rainfall
ADWF Flow
Realtime Flow
I/I Flow Rate
Response Pattern
Sharp Spike
Short Duration
Response Pattern
Gradual Increase
Gradual Recession
Response Pattern
Combination of Inflow
and Infiltration