התאמה אישית מאוחרת
במקרים רבים נדרש שהתקנים
אלקטרוניים יצאו לשוק בגרסאות שונות
- מדינות שונות או בהגדרות שפה שונות,
סט תכונות שונה, התאמות של ערוצי
.)
firmware
מכירה או גרסאות קושחה (
כך הוא למשל במקרה של מכשירים
ביתיים (מכונות כביסה, מייבשים,
מכשירי מיקרוגל, מכונות קפה), טלפונים
סלולריים, טלפונים אלחוטיים והתקנים
רבים אחרים. ברוב המקרים, החומרה
של ההתקנים האלו תהיה זהה בכל מוצרי
המשפחה, והגרסאות נקבעות רק באמצעות
נתוני תצורה המאוחסנים באזור הזיכרון
שבמעגל הראשי של ההתקן. מצב זה יוצר
דילמה בין קלות התכנות לבין הגמישות
של שרשרת האספקה: ככל שהתכנות של
הגרסה מתבצע בשלב מוקדם יותר בתהליך
הייצור, כך קל יותר לבצע אותו. עם זאת,
בהתאמה אישית מוקדמת, הגמישות של
שרשרת האספקה נפגעת מאחר שהיצרן
נדרש ליצור מלאי של כל הגרסאות ואינו
יכול להגיב במהירות לשינויים מאוחרים
.)2
יותר בדרישה (עיין באיור
מציע פתרון לדילמה זו: על ידי
RFID
בעל שני ממשקי
RFID
השימוש בשבב
ועם חיבור
RFID
תקשורת (שבב עם ממשק
) לצורך אחסון נתוני התצורה, ההתאמה
I
2
C
האישית המאוחרת הופכת לקלה בהרבה.
שנבחר,
RFID
בתלות בגודל האנטנה ובתדר
אפשר לבצע את התכנות ממרחק של כמה
מטרים, כל עוד אין סיכוך משמעותי בין
האנטנה של הקורא ובין האנטנה של התג.
כך מתאפשר ביצוע התאמה אישית (קביעת
גרסה) גם כאשר המכשיר נמצא כבר
בתוך אריזת המכירה ולכן אפשר להגיב
במהירות לשינויים בדרישה בגרסה זו או
אחרת. כתוצאה מכך גדלה הגמישות של
.)3
שרשרת האספקה (איור
המימוש של התאמה אישית מאוחרת
אינה קשה. כל שנדרש
RFID
מבוססת
בהתקן הוא שבב עם ממשק כפול כגון
ומבנהשל אנטנה, שהיא
UCODE
I
2
C
חיבור
). הפרטים
PCB
חלק מהמעגל המודפס (
לגבי המימוש מתוארים בהמשך. התדר
הנבחר עבור התאמה אישית מאוחרת דרך
,)915
MHz
עד
868
MHz
(
UHF
האריזה היא
מציע טווחי כתיבה
UHF
מפני שרק תחום
וקריאה של מטרים אחדים.
התהליך של התאמה אישית מאוחרת
. נקודת המפתח במקרה
4
מתואר באיור
«
«
«
מופעלים באמצעות השדה של הקורא/כותב ולא נדרשת
RFID
תגי
.1
איור
להם סוללה או ספק כוח אחר לצורך תקשורת
הדילמה של הגרסאות: תכנות של גרסאות מבוסס מגע יכול לחסוך
.2
איור
בעלות התכנות או לחסוך בעלות שרשרת האספקה, אך לא בשתיהן
התאמה אישית מבוססת
.3
איור
(בתצורה של אפס הספק)
RFID
קלה למימוש וחוסכת בעלויות
שרשרת האספקה
Interactive RFID and NFC Enable New Applications in Electronics
Page 1
)NFC( technology in smart phones and other mobile devices allows these to be used as HF
readers as well and therefore brings RFID more and more into the hands of consumers.
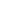
Figure 1 Passive RFID tags are powered by the reader/writer field and do not need a
battery or other power supply for communication
In the above mentioned traditional applications, the RFID tags are usually standalone cards,
tokens or adhesive labels attached to the product they identify. Also in electronic devices,
RFID track&trace is starting to spread and replace the bar codes currently used for the
identification of printed circuit boards )PCBs(. The first generations of RFID chips for PCB
tracking work like a stand-alone tag which just happens to be located on the same PCB
–
there is no connection between the RFID chip and the circuitry on the board.
A new generation of RFID chips now offers an I²C connection in addition to the antenna port,
and can therefore be connected directly to microcontrollers and ASICs. What does this mean
for electronics designers, product-, service- and production-managers? It opens completely
new possibilities for electronics during production, test and service, and can offer more
convenience to the end user.
Serial number / data
Power and commands
RFID Reader
Tag antenna
Tag / device
Interactive RFID and NFC Enable New Applications in Electronics
Page 2
Late customization
Many electronic devices need to come to the market in variants
–
different country or
language settings, different feature sets, sales channel adaptations or firmware versions.
This is the case e.g. in home appliances )washers, dryers, microwaves, coffee machines(,
cell phones, cordless phones, and many more. In most cases, the hardware of these devices
is the same for the whole product family, and the variants are only determined by
configuration data which is stored in a memory area on the main board of the device. This
creates a dilemma between ease of programming and supply-chain flexibility: The earlier in
the manufacturing process the variant is programmed, the easier this programming process
is. However, with an early customization, the supply chain flexibility suffers because the
manufacturer has to build stocks of all variants and cannot react quickly to changes i
demand later on )see Figure 2(.
Figure 2 The Variant Dilemma: Contact-based programming of variants can either
save programming cost or supply chain cost, but not both.
RFID offers a solution to this dilemma: By using a dual-port RFID chip (a chip with an RFID
interface and an I²C port( to store the configuration data, late customization becomes much
Ease of
variant
programming
E sy
(no significant extra
effort(
Diffic lt/Im ossible
(need to unpack
appliance, supply with
power(
Supply chain
flexibility
Low
(need to keep separate
stock for each variant(
High
)Keep only generic stock,
can easily react to
changing demand(
Programming during PCB
ssembly and test
Programming after final
applian e assembly / test
/ packaging
Customization p int
Early
Late
easier. Depending on the antenna size and the chosen RFID frequency, several meters of
programming range are po sible, as long as there is no significant shielding between the
reader antenna and the tag antenna. This enables the customization even when the
appliance is already in the sales packaging, and therefore it makes it possible to quickly react
to changing demand of one variant or another. As a consequence, this increases the supply
chain flexibility )see Figure 3(.
Figure 3 RFID-based late customization (zero-power configuration) is easy to
implement and saves supply chain cost.
Implementing RFID-based late customization is not difficult. All that is needed in the device is
a dual interface chip like the UCODE I²C and an antenna structure which is part of the
printed circuit board )PCB(. Details on the implementation are described in a later section.
The frequency of choice for late customization through packaging is UHF (868…915MHz),
because only UHF offers read/write ranges of several meters.
Ease of
variant
programming
Easy
(no contact interface
needed, devicecan be
unpowered(
Supply chain
flexibility
High
)Keep only generic stock,
can easily react to
changing demand(
Contactless programming
after final assemblyor
packaging
Late customization
with RFID
זה היא שהמכשיר כלל אינו מופעל בשעה
כותב את נתוני התצורה בתוך
RFID
שקורא
בעל
EEPROM
זיכרון המשתמש של זיכרון
הממשק הכפול.
הופכים את השירות ללקוח לקל
כאשר התקן אלקטרוני מוחזר לשירות או
לתיקון, יש צורך לאסוף נתונים בסיסיים
מסוימים:
• זיהוי המוצר (מספר סידורי, תאריך
הייצור, גרסת תוכנה וכיו"ב)
)
firmware
• גרסת קושחה (
• היסטוריה של שירות ותיקונים
• יומן פעילות או יומן שגיאות
מציע דרך נוחה לאסוף
RFID
בנוסף,
את הנתונים ישירות מההתקן שנדרש
לו שירות. יכולת הקריאה באפס הספק
מזיכרון בעל ממשק כפול, כפי שמוצג
, יוצרת יתרון משמעותי לעומת
5
באיור
New-Tech Magazine l 32