השיטות המשמשות כיום. להלן מפורטים
כל אחד מהפריטים:
כיום הזיהוי נעשה ברוב
זיהוי המוצר:
•
המקרים באמצעות מספר סידורי מודפס
או מוטבע עם אפשרות לברקוד. לאחר
מכן אפשר לאחזר ממסד נתונים את כל
הנתונים האחרים (תאריך ייצור, גרסת
חומרה וכיו"ב), כאשר המספר הסידורי
משמש כמפתח חיפוש. לאחזור כזה יש כמה
חסרונות: לעתים יש לפתוח את ההתקן
כדי לקבל גישה אל המספר הסידורי,
מאחר ששיקולים אסתטיים מונעים ציון
של מספר סידורי על החלק החיצוני של
ההתקן. ייתכן שהמספר הסידורי יהיה לא
קריא כתוצאה משחיקה או מפני שנעשה
ניסיון לגרד אותו כדי לזכות בדרך של
רמייה, בתיקון במסגרת האחריות לאחר
שתקופת האחריות פגה. יתרונות השימוש
: אפשר לקרוא את המספר
RFID
בזיהוי
הסידורי ללא צורך בקו ראייה ישיר, כלומר
RFID
על ידי הצבת ההתקן בקרבת קורא
מבלי לפתוח את ההתקן או לאתר ברקוד.
כך נחסך זמן רב של אנשי השירות. בנוסף,
יכול להכיל מידע נוסף על המספר
RFID
תג
הסידורי, כך שאפשר לאחסן באופן מקומי
על השבב את תאריך הייצור, גרסת החומרה
וכיו"ב ולאחזר אותם ללא התחברות אל
מסד הנתונים. לבסוף, זיהוי כזה הופך את
מעשה הרמייה בתחום השירות לקשה יותר
משובץ
RFID
באופן משמעותי, מפני ששבב
בתוך ההתקן.
על מנת לזהות את גרסת
גרסת קושחה:
•
החומרהשל התקן באופן ודאי, ההתקן חייב
להיות במצב תפקוד תקין, מחובר למקור
חשמל ופועל, החומרה המשמשת לאבחון
צריכה להיות מחוברת בתקשורת עם
ההתקן דרך חיבור השירות (למשל ממשק
אינפרה אדום או מחבר שירות). יתרונות
)
MCU
: המיקרובקר (
RFID
השימוש בזיהוי
של ההתקן כותב בכל הפעלה את גרסת
הקושחה בזיכרון המשתמש של הממשק
הכפול. באופן כזה אפשר לקרוא את גרסת
הקושחה בשלב מאוחר יותר באמצעות
, גם ללא הפעלה של ההתקן
RFID
קורא
וגם כאשר ההתקן אינו עוד במצב תפקוד
תקין.
נתונים
היסטוריה של שירות ותיקונים:
•
אלו מתועדים בדרך כלל במסד נתונים,
כשהמספר הסידורי משמש כמפתח.
: אפשר
RFID
יתרונות השימוש בזיהוי
לאחסן באופן לא מקוון חלק מהמידע לגבי
השירות והתיקונים בזיכרון המשתמש של
התקן הממשק הכפול, ולכן אפשר לגשת
אליו לצורך בדיקה בסיסית, גם כאשר
מסד הנתונים אינו זמין, למשל כתוצאה
מכך שאין חיבור לרשת.
על
יומן פעילות או יומן שגיאות:
•
מנת להקל על ביצוע האבחון ולקבל
סטטיסטיקה לגבי שימוש, התקן יכול
ליצור יומן בזיכרון פנימי, אשר בו יירשמו
ההפעלה האחרונה שהצליחה, קודי שגיאה
או סטטיסטיקה הקשורה להתקן, כגון
מונה זמן פעולה. בדומה לקריאה של
גרסת הקושחה, אפשר יהיה לאחזר את
הנתונים האלו רק אם ההתקן במצב פעולה
ובמצב תפקוד תקינים ומחובר אל חומרת
:
RFID
האבחון. יתרונות השימוש בזיהוי
המיקרובקר כותב את מידע היומן ישירות
בזיכרון של ההתקן בעל הממשק הכפול
במהלך הפעולה, וטכנאי השירות קורא את
. באופן כזה
RFID
הזיכרון באמצעות קורא
אפשר לחסוך זמן ומאמץ, מאחר ואפשר
לקרוא את יומן הפעילות ויומן השגיאות
בלי להפעיל את ההתקן, בלי לחבר אותו
ומבלי לפתוח אותו.
תקשורת דו-כיוונית
בחלק מהזיכרונות בעלי הממשק הכפול,
אפשר לקיים גם תקשורת ישירה דו כיוונית
לבין המיקרובקר.
RFID
בין הקורא/כותב
תומך במצב גשר שבו
UCODE
I
2
C
לדוגמה,
RFID
יש החלפה של נתונים בין הצד של ה-
לבין המיקרובקר דרך אוגרי הזיכרון הזמני
). למצב זה יש שלושה
buffer
register
(
יתרונות:
• הנתונים אינם מוגבלים לגודל של זיכרון
(זיכרון המשתמש
RFID
המשתמש שבתג
הוא בדרך כלל בגודל של קילוביט ספורים)
• אין הגבלה על מספר מחזורי הכתיבה
• מהירות העברה גדולה יותר בזכות כתיבה
מהירה יותר לאוגרים ומנגנון פסיקה
) שמודיע למיקרובקר כאשר
interrupt
(
קיימים נתונים זמינים
• אין צורך ליצור חיבור פיסי (שיכול
להשפיע על הממדים)
אפשר אפילו להעיר את ההתקן על ידי
. גישה
RFID
גישה אליו באמצעות קורא
«
«
«
בעל ממשק
UCODE I
2
C
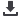
תהליך כתיבה בהספק אפס באמצעות זיכרון
.4
איור
נייח ועם
UHF
כפול. תהליך הכתיבה במקרה זה מוצג כתהליך כתיבה עם קורא
אנטנה
עם ממשק
UCODE I
2
C
תהליך קריאה באפס הספק באמצעות זיכרון
.5
איור
נייד
UHF
כפול. במקרה זה מוצג תהליך הקריאה בעזרת קורא
UHF
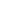
פעולה במצב גשר של זיכרון בעל ממשק כפול בדוגמה של שבב
.6
איור
UCODE I
2
C
עם ממשק
Interactive RFID and NFC Enable New Applications in Electronics
Page 3
into the user memory of the dual-interface EEPROM.
Figure 4 Zero-power write process, using the UCODE I²C dual-interface memory. Here
the write process with a stationary UHF reader plus antenna is shown.
MCU
Data
Step 1
•
Device is unpowered
•
Write data from UHF reader/writer into
UCODE I²C user memory
Appliance
MCU
Data
Step 2
•
Power-up device
•
MCU reads the data from the UCODE I²C
user memory
Appliance
Interactive RFID and NFC Enable New Applications in Electronics
Page 5
Advantage with RFID
: The MCU writes the log information directly into the dual-
interface memory during operation, and the service technician reads th
ry out
with an RFID reader. This saves time and effort, as the activity and error log can be
read out without powering, connecting or opening the device.
Figure 5 Zero-power read process using the UCODE I²C dual-interface memory. Here
the read process with a hand-held UHF reader is shown.
Bidirectional communication
With some dual-interface memories, even direct bidirectional communication between an
RFID reader/writer and the MCU is possible. For example, the UCODE I²C supports a bridge
mode, in which data is exchanged between the RFID side and the MCU through buffer
registers. The bridge mode has three advantages:
Data is not limited to the user memory size of the RFID tag )user memory is a few
kbits usually(
No limitation on write cycles
Higher transfer speed due to faster writes to registers and an interrupt mechanism
which alerts the MCU once data is available
No need to make a physical connection )that could influence the measurements(
It is even possible to wake up a device by approaching it with an RFID reader. This creates
an interrupt signal upon a first register write from the UHF reader/writer even when the
device is in sleep mode, thereby conserving energy during the inactive time. The principle of
bridge mode operation is shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6 Bridge-mode operation of a dual-interface memory at the example of the UHF
chip UCODE I²C
MCU
Data
Step 2
•
Data can be read anytime by a UHF reader
even when the device is unpowered
MCU
Data
Step 1
•
MCU writes data into UCODE I²C user
memory
Appliance
Appliance
MCU
Step 1
•
Bring a UHF reader/writer to the device
(powered or unpowered(
•
The field-detect function wakes up the device
Step 2
•
The device is now powered
•
Exchange data between the UHF reader/writer
and MCU directly through buffer registers
Data
MCU
Appliance
Field detect
interrupt
Appliance
Interactive RFID and NFC Enable New Applications in Electronics
Page 5
Figur 5 Zero-power read process using the UCODE I²C dual-interface memory. Here
the read process with a hand-held UHF reader is shown.
Bidirectional communication
With some dual-interface memories, even direct bidirectional communication between an
RFID reader/writer and the MCU is possible. For example, the UCODE I²C supports a bridge
mode, in which data is exchanged between the RFID side and the MCU through buffer
registers. The bridge mode has three advantages:
Data is not limited to the user memory size of the RFID tag )user memory is a few
kbits usually(
No limitation on write cycles
Higher transfer speed due to faster writes to registers and an interrupt mechanism
which alerts the MCU once data is available
No need to make a physical connection )that could influence the measurements(
It is even possible to wake up a device by approaching it with an RFID reader. This creates
an interrupt signal upon a first register write from the UHF reader/writer even when the
device is in sleep mode, thereby conserving energy during the inactive time. The principle of
bridge mode operation is shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6 Bridge-mode operation of a dual-interfac memory at the example of the UHF
chip UCODE I²C
MCU
Data
Step 2
•
Data can be read anytime by a UHF reader
even when the device is unpowered
MCU
Data
Step 1
•
MCU writes data into UCODE I²C user
memory
Appliance
Appliance
MCU
Step 1
•
Bring a UHF reader/writer to the device
(powered or unpowered(
•
The field-detect function wakes up the device
Step 2
•
The device is now powered
•
Exchange data between the UHF reader/writer
and MCU directly through buffer registers
Dat
MCU
Appliance
Field detect
interrupt
Appliance
Interactive RFID and NFC Enable N w Applicat ons i Electronics
Page 5
Advant ge with RFID
: The MCU writes the log information directly into the dual-
interface memory during operation, and the s rvice technician reads the me ory ut
with an RFID read r. This saves time and effort, as the activity and error log can be
read out wi hout powering, connecting or opening the d vic .
Figure 5 Zero-p wer r ad process u ing the UCODE I²C dual-interface me ory. Here
the read process with a h nd-held UHF read r is shown.
Bidirectional communication
With some dual-interface m ories, ven direct bidirectional communicat on betw en a
RFID read r/write and the MCU is possible. For example, the UCODE I²C supports a bridge
mode, in whic data is exchanged betw en the RFID side and the MCU through buffer
register . The bridge mode has three adv nt ges:
Data is not limited o the user me ory size of the RFID tag )user me ory is a few
kbits u ually(
No limitation write cycles
Highe transfer speed due to faster writes o register and an interrupt mechanism
which alerts the MCU once data is available
No need to make a physical onnection )that could influenc th m asurem nts(
It is even possible to wake up a devic by approaching t w h an RFID read r. This creat s
an interrupt signal upon a first register write from the UHF read r/write even when the
device s in sleep mode, thereby conserving energy during the inactive time. The principle of
bridge mode operation s shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6 Bridge-mode operation f a dual-interface m ory at the example of the UHF
chip UCODE I²C
MCU
Data
Step 2
•
Data can be read anytime by a UHF read r
even when the d vic s unpowered
MCU
Data
Step 1
•
MCU writes data into UCODE I²C user
me ory
Appliance
Appliance
MCU
Step 1
•
Bring a UHF read r/writer to the devic
(powered or unpowered(
•
The field-detect function wakes up the devic
Step 2
•
The devic is now powered
•
Exchange data betw en the UHF read r/writer
and MCU directly through buffer r gister
Data
MCU
Appliance
Field detect
interrupt
Appliance
New-Tech Magazine l 34