with the respective multiple comparisons tests and the non-
parametric model when necessary (median, minima, and
maxima values). Means and standard deviations of each
group were presented when the parametric model was used.
For the nonparametric model, medians and their minimum
and maximum values were presented, considering the 5%
significance level (
P
\
.05) within each age range.
Results
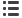
The starting point in our study was to analyze H&E slides
to check the syntopy of the lamina propria structures in
vocal folds and then perform the immunohistochemical
study. In these images (
Figure 2
), it was possible to
observe in the control group adults that collagen fibers are
arranged as a loose fabric between some fibroblasts and ves-
sels in the entire vocal fold lamina propria. In the 60- to 75-
year-old group subjects, it was possible to identify a dense
collagen thickness deposited on the subepithelial layer
(
Figure 2B
). Finally, in the elderly group (greater than 75
years of age), dense collagen uniformly occupied the whole
lamina propria (
Figure 2C
).
The immunoexpression of antibodies for collagens I, III,
and elastin as well as collagens IV and V is presented in
Tables 1
and
2
, respectively, and shown in
Figures 3
to
7
.
We observed that, for collagen I and III, there was an
increase of labeling density in the elderly larynges, without
any statistical difference between elderly subgroups.
Regarding collagens IV and V, a greater labeling density was
observed in the endothelium of vessels of the lamina propria
and basement membrane. Finally, regarding elastin, we
observed a decrease of this antibody as the age increased in
both elderly groups.
Discussion
Presbyphonia is a physiological effect of the senescence
process that takes place in the whole body. Trying to
Table 1.
Immunoexpression of Antibodies for Collagens I, III, and Elastin, Measured as Area Percentage (%).
a
Antibodies
Collagen I
Collagen III
Elastin
Age Group, y
SL
DL
P
Layers
SL
DL
P
Layers
SL
DL
P
Layers
30-50
34.2 (8.5)
3.8 (10.4) .105 25.6 (21.6-29.4) 23.6 (20.5-29.9) .046 28.2 (25.7-29.3) 27.5 (23.6- 33.3) .508
60-75
39.6 (5.1) 44.4 (7.5)
.114 31.2 (23.7-35.6) 24.6 (20.1-29.7) .0051 20.8 (19.2-23.7) 23.0 (18.7-28.2)
.114
.
75
40.4 (5.7) 46.9 (9.3)
.114 32.4 (24.8-44.4) 29.9 (22.1-40.1) .333 15.9 (10.8-24.3) 18.2 (14.3-25.9)
.285
P
ages
.002
*
.0061
*
.00001
*
a
Mean (standard deviation) or median (minimum and maximum) according to age group and depth of vocal folds lamina propria. DL, deep layer; SL, superficial
layer.
*
P
with statistical significance.
Figure 2.
(A) Control group: collagen fibers in the lamina propria, some fibroblasts and vessels. (B, C) Elderly groups: dense collagen in
the lamina propria and thickened basement membrane. Hematoxylin and eosin, 10
3
.
Table 2.
Immunoexpression of Antibodies for Collagens IV and V,
Measured as Area Percentage (%).
a
Collagen IV
Collagen V
Age Group, y
SL
DL
SL
DL
30-50
20.9 (2.9) 17.6 (3.7) 38.5 (14.4) 36.6 (8.5)
60-75
20.7 (4.4) 19.3 (4.2) 36.2 (8.9)
35.0 (5.6)
.
75
21.3 (3.9) 20.4 (3.5) 31.8 (5.6)
31.3 (6.0)
P
ages
.573
.2597
P
Layers
.0034
.397
a
Mean (standard deviation) according to age group and depth of vocal folds
lamina propria. DL, deep layer; SL, superficial layer.
*
P
with statistical significance.
Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery 152(2)
81