allows quantitative evaluation of spatial characteristics of fre-
quency and phase. In the present study, the incidence of diplo-
phonia and lateral/longitudinal phase difference normalized by
glottal cycle (N
G
-lateral/longitudinal phase difference) were
evaluated.
12
Image sequence of 512 frames was evaluated.
The SLK analyzes mediolateral vocal fold movements at a
midglottal level and allows evaluation of mediolateral and tem-
poral vibratory characteristics such as amplitude (N
L
-amplitude
mean), mucosal wave (N
L
-mucosal wave magnitude mean),
phase (N
G
-lateral phase difference and N
G
-longitudinal phase
difference), open quotient (O
q
SLK
), speed index (SI
SLK
), and in-
tegral glottal width (N
GL
-integral glottal width).
13
Image
sequence of 400 frames was evaluated.
The MLK involves five different longitudinal levels, and can
assess temporal and longitudinal oscillatory features such as
open quotient (O
q
MLK
), speed index (SI
MLK
), and opening/clos-
ing longitudinal phase difference (N
G
-opening/closing longitu-
dinal phase difference).
14
Image sequence of 400 frames was
evaluated.
The GAW provides information on the general dynamics of
the glottal area by tracing the vocal fold edges and displaying
temporal changes of the glottal area, with which open quotient
(O
q
GAW
), speed index (SI
GAW
), minimal glottal area (N
L
-mini-
mal glottal area), maximal glottal area (N
L
-maximal glottal
area), glottal outlet (N
L
-glottal outlet), and glottal area differ-
ence (glottal area difference index
¼
(N
L
-maximal glottal
area N
L
-minimal glottal area)/N
L
-maximal glottal area) can
be evaluated.
15
Five consecutive glottal cycles of the most sta-
ble segment were evaluated (100–200 frames).
All the HSDI analyses were performed with custom
MAT-
LAB
software (Version 2011a; Mathworks, Inc., Natick, MA)
programmed at our institution . An example of HSDI analysis
is shown in
Figure 1
.
Statistics
The difference of clinical and HSDI parameters between VFA
patients and vocally healthy subjects were evaluated by Stu-
dent’s
t
test for normally distributed parameters, or either by
the Mann-Whitney
U
test or by chi-squared test for other pa-
rameters. To assess the correlations with HSDI parameters
and reference data (demographic, aerodynamic/acoustic, or
stroboscopic data), or the correlations among HSDI parameters,
Pearson’s correlation analysis for normally distributed parame-
ters and Spearman’s correlation analysis for the other parame-
ters were used. In all analyses,
P
value lower than 0.05 was
considered significant. Calculations were performed with a
custom
MATLAB
software.
RESULTS
HSDI parameters in the VFA
Frame-by-frame analysis.
The glottal gap was observed in
45% of the VFA group and 30% of the control group
(
P
¼
0.235), and the most frequent type was spindle shaped
for the VFA group (47.8% of those with glottal gaps) and ante-
rior for the control group (66.7% of those with glottal gaps).
Although no parameters revealed significant differences be-
tween the two groups, the VFA group tended to demonstrate
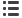
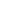
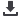
FIGURE 1.
An example of the analysis of high-speed digital image is shown. (
A
–
D
) Laryngotopography is shown. (
A
) A static laryngeal image to be
superimposed by analyzed topographic data. (
B
–
D
) Spatial distribution of amplitude, frequency, and phase of the maximum amplitude components,
respectively. This 71-year-old female patient has a topographic F0 of 225 Hz, left-to-right lateral phase difference (6.3% of a glottal cycle), and
anterior-to-posterior longitudinal phase difference (21.9% of a glottal cycle). (
E
–
H
) Glottal area waveform is shown: areas demarcated by a green
line in Panels (
E–H
) show a minimal glottal area, a maximal glottal area, and a glottal outlet, respectively; and a green line in Panel (
G
) signifies the
vocal fold length. This patient has an anterior glottal gap with a N
L
-minimal glottal area of 1.2%, a spindle-shaped maximal glottal area with a N
L
-
maximal glottal area of 11.5%, and no supraglottal hyperfunction with N
L
-glottal outlet of 100.2%. (
I
) Multi-line kymography is shown. There are
anterior-to-posterior opening and posterior-to-anterior closing longitudinal phase differences (23.8% and 19.0% of a glottal cycle, respectively). O
q
MLK
and SI
MLK
are 0.86 and 0.21, respectively.
Akihito Yamauchi,
et al
HSDI Analysis of VFA
92