Chapter 3
64
DISCUSSION
In this study we compared the VCO
2
values by IC (Deltatrac®) and ventilator (Servo-I®) in 41
mechanically ventilated critically ill children; VCO
2
values were highly correlated, but not
comparable due to underestimation of VCO
2
values by the Servo-I®. 95% limits of agreement in
the Bland-Altman analysiswerewide, showingpoor agreement. Clinically useful measurements
(difference ≤10% between VCO
2
values of the Servo-I® and those of IC) were seen in children
with higher weight. In the 20 children weighing ≥15 kg, VCO
2
measurements were comparable
between IC and Servo-I® and the derived REE values were more precise than predominantly
used predictive equations with a smaller difference and narrower limits of agreement. In 81%
of the children weighing <15 kg, measurements by the Servo-I® deviated >10% from those of
IC, which made the use of measurements in these children very limited.
The wide limits of agreement may be due to the technical specifications of the sampling
methods; especially the underestimation by the Servo-I® in children <15 kg may be affected
by the characteristics of the sensor. VCO
2
is the volume of eliminated CO
2
calculated over
one minute. CO
2
is mainly measured in the exhaled breath of alveoli (phase 2 and 3 of the
capnogram, Fig 4), while breath from the upper airways is void of CO
2
(dead space, phase 1 of
capnogram).
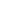
Figure 4.
Capnogram divided in 4 phases. Phase I represents airway dead space. It is the CO
2
-free portion
of the exhaled breath from the conducting airways. Phase II (expiratory upstroke) represents the mixing of
airway dead space gas with alveolar gas, and is characterised by a significant rise in CO
2
. The steep slope is
due to fast-emptying alveoli. Phase III is the alveolar plateau; it reflects the level of effective ventilation of
the alveoli. The gradual rise in the slope is due to late-emptying alveoli. Phase IV is the inspiratory down
stroke, the beginning of the next inspiration