102
Chapter 5
adulthood, we assessed the effect of reward motivation on cognitive control across the life
span, from adolescence (prior to the start of age-related decreases) to senescence.
Methods
Participants and procedure
Pooling the data from five studies that were conducted between 2008 and 2015 enabled us
to include 118 healthy participants (63 men, mean age 35.03, range 14-69). Three of these
studies (N = 60) were conducted in a functional magnetic resonance environment: one in
healthy young participants
(Aarts et al., 2010) and the other 2 were patient studies (e.g. Aarts
et al., 2015). We only included the healthy control participants who participated in these
patient studies. The remaining participants were 26 (Aarts et al., 2012) and 32 healthy control
participants who were tested in front of a computer screen (
table
5.1
). All studies were
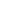
Table 5.1
Characteristics of participants and studies
Study A
Study B
Study C
Study D
Study E
Total
N
32
24
27
9
26
118
Age mean
15.44
21.92
38.78
58
59.58
35.03
Age range
14-17
18-27
24-65
29-67
42-69
14-69
Gender (% men)
59.4 %
41.67 %
44.44 %
77.78 %
57.69 %
53.4 %
Max
possible
reward
€ 12.80
€ 8.80
€ 12.80
€ 12.80
€ 13.20
High reward
€ 0.15
€ 0.10
€ 0.15
€ 0.15
€ 0.10
Earned
bonus:
mean (SE)
€ 9.10
(34.05)
€ 7.17
(17.45)
€10.38
(22.09)
€ 10.04
(61.40)
€ 12.05
(12.32)
€ 9.72
(19.50)
Earned bonus:
% of max: mean
(SE)
71.28 %
(2.62)
81.49%
(1.98)
81.10 %
(1.73)
78.44
%(4.80)
91.29% (0.89)
80.56%
(1.18)
Number of trials
160
160
160
160
240
Type of study
Behavioral
control
group
patient
study
fMRI
young
healthy
participants
fMRI
control
group
patient
study
fMRI
control
group
patient
study
Behavioral
control group
patient study
ITI
and
RC
interval
1-2s
2-6s
2-6s
2-6s
1-2s
CT interval
400 msec.
2-6s
400 msec.
400 msec.
1-2s
SE = standard error; ITI = inter-trial-interval; RC = reward - task cue; CT = task cue - target.