UPM Annual Report 2014
UPM Annual Report 2014
13
14
CONTENTS
Financial targets
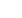
At the business area level, UPM targets top
relative performance in their respective markets
compared with key peers. UPM has also
defined long-term EBITDA margin and ROCE
targets for each of its business areas. In the case
of UPM Paper ENA, these long-term targets
are instead defined for cash flow margin and
cash flow return on capital employed.
In UPM Energy, where the asset base is
valued at fair value, the ROCE target is 6%.
In the less capital intensive converting industry,
UPM Raflatac, the ROCE target is 18%. Final-
ly, in the process industry businesses UPM
Biorefining, UPM Paper Asia and UPM Ply-
wood, the ROCE target is 10-12%, or cash
return in the case of UPM Paper ENA.
With the current business portfolio, achiev-
ing the business area targets simultaneously
would result in a UPM Group operating profit
margin of approximately 10%, and ROCE of
approximately 9%.
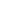
At the Group level, UPM’s financial targets
are based on return on equity and gearing. The
return on equity target is at least five percentage
points above the yield of a 10-year risk-free
investment such as the Finnish government’s
euro-denominated bonds. At the end of 2014,
the minimum target for return on equity, as
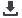
defined above, was 5.9%. The gearing ratio is
to be kept below 90%. For 2014, UPM’s return
on equity excluding special items was 8.3% and
gearing was 32% at the end of the year.
Earnings sensitivities
Changes in sales prices
The biggest factor affecting UPM’s financial
results is the sales price of paper. A change in the
volume delivered has less than half of the effect
of the same percentage change in sales prices.
EFFECT OF A 10% CHANGE IN PRICES
ON OPERATING PROFIT FOR THE YEAR
EURm
Papers in UPM Paper ENA
509
Fine and speciality papers in
UPM Paper Asia
90
Label materials
125
Plywood
40
Sawn timber
29
Chemical pulp (net effect)
18
FOREIGN CURRENCY NET CASH FLOW
EURm
USD
810
GBP
500
JPY
160
Others, total
170
COSTS, EXCLUDING DEPRECIATION
%
2014 2013
Delivery of own products
10 11
Wood and fibre
31 29
Energy
9 10
Fillers, coating and chemicals
11 12
Other variable costs
14 13
Personnel expenses
15 15
Other fixed costs
10 10
Total
100 100
Costs totalled EUR 8.7 billion in 2014
(2013: 9.1 billion)
Changing exchange rates can also have
indirect effects, such as change in relative
competitiveness between currency regions.
Cost structure
The company’s biggest cost items are the cost
of fibre raw material and personnel expenses.
Risk management
Risk description
Impact
Management
STRATEGIC
RISKS
Structural changes in paper usage
result in decline in paper demand which
leads to overcapacity
Continuously operating rates and weak
pricing power in the industry
Ensure cost efficiency of operations
Proactive product portfolio management
Delay in OL3 nuclear plant start-up and
consequent loss of profit and cost overruns
Material cost overrun
Ensure that contractual obligations are
met by both parties
Arbitration proceedings have been initiated
by both parties
Cost of an acquisition proves high and/
or targets for strategic fit and integration
of operations are not met
Return on investment does not meet targets
Disciplined acquisition preparation to ensure
the strategic fit, right valuation and effective
integration
Regulatory changes such as EU climate
policy and new requirements for CO
2
emissions
Subsidies for alternative uses of wood
raw material increase costs
Changes to relative competitiveness
of energy forms
Communicate the employment and value-
added creation impacts of such policies clearly
Invest in new, value-adding uses of biomass
Cost competitive operations
OPERATIONAL
RISKS
Availability and price of major
production inputs like chemicals, fillers
or roundwood
Increased cost of raw materials and potential
production interruptions would lower
profitability
Improving materials efficiency
Long-term sourcing contracts and relying
on alternative suppliers
Ownership of forest land and long-term
forest management contracts
Execution of investment projects
Material cost overrun, return on investment
does not meet targets
Disciplined planning, project management
and follow-up processes
Ability to retain and recruit skilled
personnel
Business planning and execution impaired,
affecting long-term profitability
Competence development
Incentive schemes
Availability of information systems
Interruptions in critical information services
cause a major interruption of UPM business
Technical, physical and process improvements
to mitigate availability risk
FINANCIAL
RISKS
Major trading currencies like USD
move significantly against euro
Changes in currencies change profitability
of exports and relative competitiveness of
currency areas
Hedging net currency exposure
on a continuous basis
Hedging the balance sheet
Payment default or customer bankruptcy
Loss of income
Active management of credit risks and
use of credit insurance
HAZARD
RISKS
Environmental risks;
A leak, spill or explosion
Damage to reputation, possible sanctions
Direct cost to clean up and to repair potential
damages to production unit, loss of production
Maintenance, internal controls and reports
Certified environmental management systems
(ISO 14001, EMAS)
Physical damage to the employees
or property
Harm to employees and damage to reputation
Damage to assets or loss of production
Occupational health and safety systems
Loss prevention activities and systems
Emergency and business continuity procedures
UPM’s business operations are subject to various risks which may have an adverse
effect on the company. The list below is not complete but it explains some of
the risks with their potential impacts and how UPM manages those risks today.
1)
1)
A more detailed description of risks and risk management is included
in the Report of the Board of Directors on page 70.
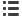
14
13
12
11
10
12
9
6
3
0
■
Operating profit excluding
special items, %
Operating profit excluding
special items
% of sales
14
13
12
11
10
12
9
6
3
0
■
ROE excluding special items, %
Minimum target
ROE compared with target
%
14
13
12
11
10
4,500
3,600
2,700
1,800
800
0
Net debt and gearing
EURm
Gearing %
■
Net debt
Gearing ratio
Gearing limit
90
72
54
36
18
0
Exchange rate risk
Changes in exchange rates over a prolonged
period have a marked impact on financial
results.
It is the company’s policy to hedge an aver-
age of 50% of its estimated net currency cash
flow for 12 months ahead.
At the end of 2014, UPM’s estimated net
currency flow for the coming 12 months was
EUR 1,640 million. The US dollar represented
the biggest exposure, at EUR 810 million.
20
16
12
8
4
0
Achievement of the long-term return targets in 2013–2014
ROCE %
*
)
ROCE %
ROCE %
CF/CE %
**)
ROCE %
ROCE %
2013 2014
UPM Energy
2013 2014
UPM Biorefining
2013 2014
UPM Paper Asia
2013 2014
UPM Paper ENA
2013 2014
UPM Plywood
2013 2014
UPM Raflatac
**)
cash flow after investments, changes in working capital and restructuring payments
*)
shareholdings in UPM Energy valued at fair value
Target