FROZEN HEAT
12
Resource occurrences and potential for recovery are not ame-
nable to an easy or simple quantification. Energy resource
assessments typically include at least three interrelated com-
ponents: geological knowledge, economics, and technology.
Increases in geological knowledge and improvements in
technology, motivated largely by increasing prices, have con-
tributed to an increase in the fossil energy resource base. The
additional resources include new fields discovered within al-
ready-established resource elements, as well as entirely new
resource elements (such as ultra-deep-water hydrocarbon re-
sources and a variety of unconventional resources) that were
previously unknown or considered non-recoverable.
A number of terms related to resources and reserves have
specific meaning in connection with hydrocarbons. The to-
tal volume of a resource, often called the in-place resource,
includes all hydrocarbons present within a given geologic
unit or geographic area. The subset of in-place resources
that is practically producible is often called the technically
recoverable resource (TRR). Those technically recoverable
resources that can be produced at a profit are economically
recoverable resources (ERR). Economically recoverable re-
sources that have been confirmed and quantified by hydro-
carbon production are called reserves (see Text Box 1.1 for
more detail).
1.2
GLOBAL ENERGY RESOURCES
AND GAS HYDRATES
Source: Johnson 2011
Former Soviet
Union
Other
Paci c Asia
Other East
Asia
Other
South Asia
Arctic Ocean
Europe
Latin America and
the Caribbean
Southern Ocean
United States
Canada
Western and
Central Africa
Southern
Africa
North
Africa
Eastern
Africa
India
Oceania
Japan
China
Middle East
196
Resource potential
Median tcf
100
50
5
Gas hydrates resource potential by global regions
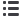
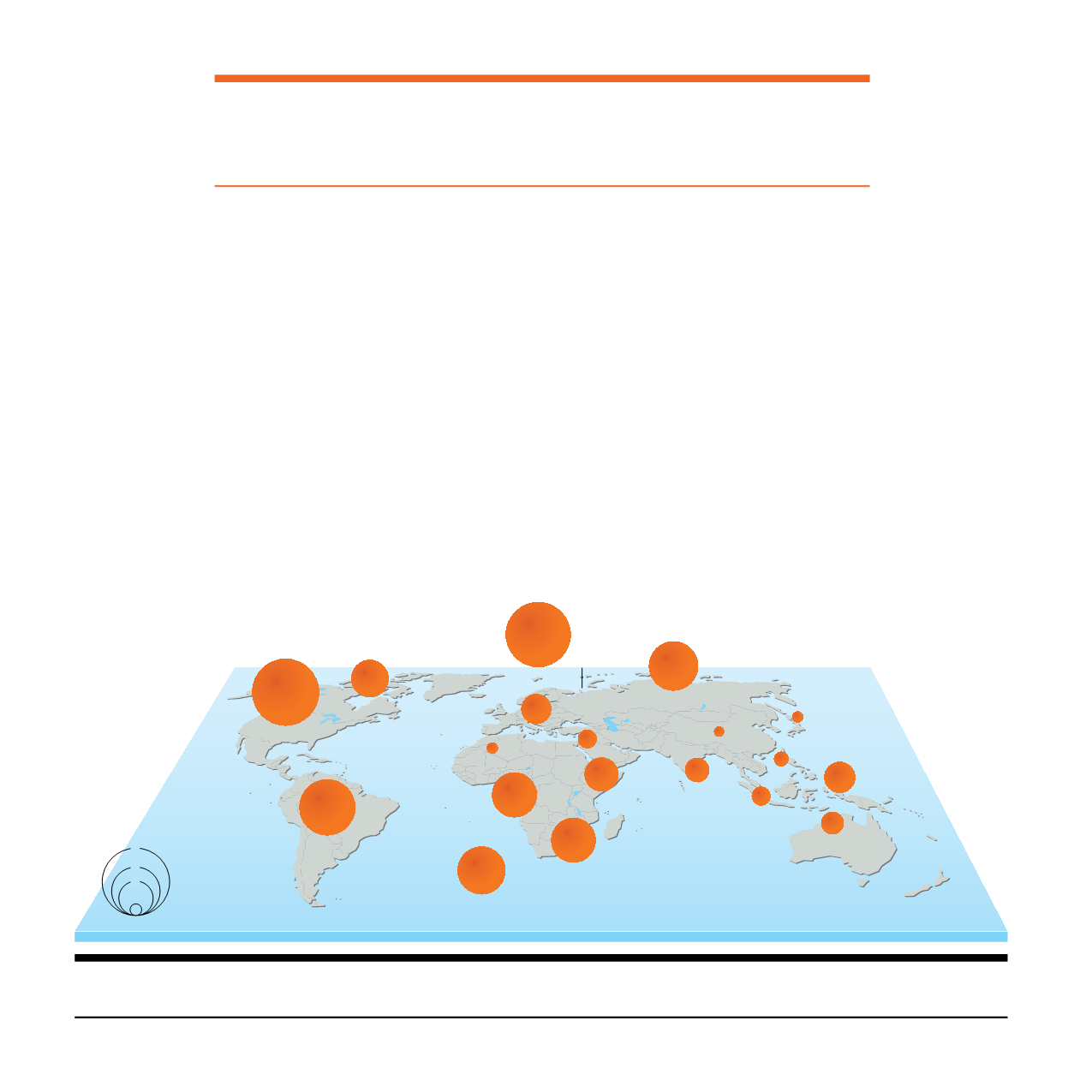
Figure 1.1:
Gas hydrates resource potential by global regions. This figure includes only that subset of global in-place gas hydrates that
appear to occur at high concentrations in sand-rich reservoirs, the most likely candidates for development. Source: Johnson 2011.
Source: Johnson 2011
Former Soviet
Union
Other
Pacific Asia
Other East
Asia
Other
South Asia
Arctic Ocean
Europe
Latin America and
the Caribbean
Southern Ocean
United States
Canada
Western and
Central Africa
Southern
Africa
North
Africa
Eastern
Africa
India
Oceania
Japan
China
Middle East
Resource potential
Median tcm
0.1
Gas hydrates resource potential by global regions
3
2
6