22
Chemical Technology • November/December 2016
T
he challenge consisted of supporting a wide range
of wireless environmental measurements using a
sing
le device that provides robotic control, remote
configuration, and data sharing over the Web for a mea-
surement system that researchers use to characterise
the forest understory microclimate and fluxes of car-
bon between the rain forest floor and the atmosphere.
Using National Instruments (NI) LabVIEW software and
NI CompactRIO hardware, researchers developed a wire-
less sensor system that collects a variety of environmental
measurements, offers remote configuration capabilities,
permits future expansion, and gives researchers around
the world access to the measurements over the Internet.
Approximately 70% of solar energy is absorbed by the
Earth’s atmosphere. As the Earth’s surface emits this
energy in the form of thermal radiation, the atmosphere
naturally captures and recycles a large portion of it, keeping
the planet warm. This process is known as the greenhouse
effect. Recently, the greenhouse effect has been artificially
enhanced by the increased emission of gases that absorb
infrared radiation such as carbon dioxide (CO
2
), methane,
and nitrous oxide. The increased absorption of thermal
radiation may contribute to the Earth’s climate change
known as global warming.
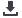
Conducting carbon flux research in the
Costa Rican rain forest
To better understand the impact of the emission of green-
house gases on the environment, researchers are conduct-
ing a study at La Selva Biological Station in the Costa Rican
rain forest to measure the exchange of CO
2
(als
o known
as the carbon flux) and other materials between the for-
Environmental monitoring
in the rain forest of
Costa Rica
by Dr William Kaiser, Department of Electrical Engineering, UCLA and Dr Philip Rundel,
Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, UCLA, Los Angeles, California
To better understand the impact of the emission of greenhouse gases on
the environment, researchers are conducting a study at La Selva Biological
Station in the Costa Rican rain forest to measure the exchange of CO
2
(also
known as the carbon flux) and other materials between the forest floor and
the atmosphere.
CONTROL AND INSTRUMENTATION