FROZEN HEAT
44
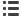
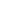
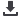
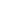
Figure 2.5:
Cold-seep organisms. Examples from the methane seep ecosystem. A, C, E and F are chemosymbiotic animals whose energy source
is hydrogen sulfide produced by methane-degrading microorganisms in the sediment. A: vestimentiferan tubeworm –
Lamellibrachia barhami
, B:
lithodid crab embracing tube cores placed in a field of vesicomyid clams and bacterial mat C: solemyid clam –
Acharax
sp. D: Snail –
Neptunea
amianta
and their egg towers attached to rock. E: Yeti crabs –
Kiwa puravida
, the ‘fur’ on their claws is filamentous symbiotic bacteria which they
nourish by waving in sulphide-rich fluids, and then consume F: Thyasiridae, Quepos Seep (400 m water depth), Costa Rica margin G: Alvinocarid
shrimp, Mound 12, Costa Rica margin (1 000 mwater depth) (Photos courtesy of Greg Rouse and Lisa Levin, Scripps Institution of Oceanography).
A
E
B
C
F
D
G