The ability of the SSL4101T to
support very-low input power in
standby mode eliminates the need
for an additional housekeeping
power supply to power the lighting
controllers or dimmers.
Although design for LED smart
lighting involves more complex power
conversion than dimming control
for incandescent lamps, integrated
devices such as the FL7701 and
SSL4101T can ease the design
burden and achieve high efficiency.
to almost zero, is controlled down by
a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO).
During frequency reduction mode,
the primary peak current is kept at
a minimal level of 25 percent of the
maximum. In frequency reduction
mode the PFC controller is switched
off as the harmonics generated will
be minimal. To prevent oscillation
around the PFC-operation point, the
device supports approximately 50
mV of hysteresis on the control pin.
slowly from initial startup. A similar
soft-start feature is available on the
SSL4101T Greenchip III+ from NXP.
On this device, the soft-start period
is determined through selection of an
external resistor and capacitor.
Able to work with conventional triac
dimming techniques, and so support
systems that need to handle a mixture
of lighting sources, the SSL4101T was
designed to provide high efficiency at
all power levels; using a variety of
PWM control techniques to suit the
conversion to the desired output light
level. The device moves from quasi-
resonant operation at high power
levels to quasi-resonant operation
with valley skipping through to
reduced-frequency operation at low
power-output levels, reducing the
current supplied to the LED to avoid
generating audible noise from the
ballast’s transformer.
In quasi-resonant mode, the next
converter stroke is started after
demagnetization of the transformer
that should be provided as part of the
front-end circuitry to the SSL4101T.
This helps to minimize losses, as the
converter only switches on when
the voltage across the external
MOSFET is at its minimum. To
reduce the frequency of operation
at lower loads, the quasi-resonant
operation changes to discontinuous
mode operation with valley skipping
in which the switching frequency is
limited for EMI reasons, typically to
around 125 kHz. Again, the external
MOSFET is only switched on when
the voltage across the MOSFET is at
its minimum.
At very low-power and standby levels,
the frequency, which can be reduced
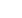
Figure 3: Block diagram of the SSL4101
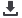
Figure 2: The FL7701 in a typical application