108
Zimbabwe is located between the Zambezi and
Limpopo rivers, situated primarily on a high
plateau that stretches across most of the country
and has a subtropical climate tempered by the
altitude. Savannah is the dominant ecosystem,
withmontane forest in the eastern highlands. The
economy is based primarily on agriculture, as well
as mining and tourism. Together with Zambia,
Zimbabwe is home to the Victoria Falls along
the course of the Zambezi River. Victoria Falls is
protected as a UNESCO world heritage site.
Progress towards environmental
sustainability
Reverse the loss of environmental resources
Zimbabwe’s major environmental challenges
are soil erosion and deforestation, as well as
urban air pollution caused by vehicle and
industrial emissions, and water pollution from
mining, domestic waste and a high use of
fertilizers (Government of Zimbabwe 2010).
About 40 per cent of land was considered
moderately degraded in 2003, with the regions
of greatest concern in the north and east where
topsoil losses of more than 100 metric tonnes
per hectare have been recorded (FAO 2004).
The major drivers of land degradation are
overgrazing and deforestation.
Zimbabwe has few perennial rivers and no large
natural lakes, and as such a network of over 8
000 dams make up the most significant surface
water resource, in addition to the large artificial
lake created by the Kariba dam. However
siltation is reducing dam capacity and poor
infrastructure hampers water access.
Despite being a low emitter, there is observed
climate variability in Zimbabwe. There has been a
noted shift in agricultural seasons, as evidenced
by late onset and sometimes late cessation
of the rainy season. In the rural areas, highly
variable rainfall and drought are challenges to
environmental sustainability. Between 1991
and 1997, Zimbabwe experienced three major
droughts that necessitated the importation of
food (SADC/SARDC and others 2008). Figure 4.50
shows the change inmaize production 1999-2007.
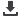
Zimbabwe
Total Area of Country
Portion of Country within Zambezi Basin
National Population in 2010
Portion of National Populationwithin Zambezi Basin
Important environmental issues
390 759 sq km
215 800 (55.2%)
13.5 million
9 059 850 (67.11%)
• Land degradation and deforestation
• Water access and drought
• Biodiversity threats, including poaching
of wildlife such as the black rhinoceros
Z
AMB
E
Z
I
RIVER BA
SI
N
L
IM
I
T
Z
A
MBEZI
R
IV
E
R
BASIN LIM
IT
Lake
Kariba
Kadoma
Kwekwe
Gweru
Bulawayo
Zvishavane
Masvingo
Chiredzi
Beitbridge
Mutare
Shamva
Mazowe
HARARE
Chitungwiza
Chinhoyi
Karoi
Hwange
Gwanda
Plumtree
Victoria Falls
MOZAMBIQUE
NAMIBIA
BOTSWANA
SOUTH AFRICA
ZAMBIA
ZIMBABWE
S
h
a
n
g
a
ni
U
m
z
i
n
g
w
a
n
i
S
a
v
e
M
a
z
o
e
Z
a
m
b
e
z
i
Elevation
Metres above
sea-level
0
200
500
1 000
3 000
2 000
1 500