104
Zambia is a landlocked country resting on
a high plateau with a subtropical climate
characterized by a single rainy season. Savannah
is the dominant ecosystem and covers the
centre of the country, separating the rain forest
in the northwest from the semi-desert region
in the southwest. Along Zambia’s border with
Zimbabwe, the Zambezi River flows over the
famous Victoria Falls –
Mosi oa Tunya
in the local
Tonga language, “the Smoke that Thunders”.
The two countries also share the Kariba Dam,
built to generate hydroelectric power and
also now a major recreation and fisheries area.
Northern Zambia joins the southern end of
Lake Tanganyika. Zambia is the source of the
Zambezi River, which rises as a small spring in
the northwest of the country.
Progress towards environmental
sustainability
Reverse the loss of environmental resources
Copper mining has played a major role in
the national economy since mining began
in the late 1920s and the rich reserves of the
Copperbelt region have made Zambia a world
leader in copper production. However, the
absence of effective environmental regulation
of the industry has led to widespread air,
soil and water pollution, through the use of
environmentally damaging mining methods
such as open pit and underground digging, as
well as pumping and disposal of large volumes
of wastewater, and smelting operations that
emit sulphur dioxide (UNEP 2008). Zambia’s
Nchanga mine is the largest opencast mine in
Africa and second largest in the world.
The capital city, Lusaka, continues to be the main
destination for rural migrants, closely followed
by Copperbelt province, together accounting
for 69 per cent of the total urbanization (UN-
HABITAT 2007). The major urban areas are faced
with serious environmental challenges such as
soil erosion, loss of soil fertility, and changes to
the microclimate resulting from illegal quarrying,
illegal development, deforestation, and the
overexploitation of forest resources (Government
of Zambia 2008).
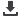
Zambia
Total Area of Country
Portion of Country within Zambezi Basin
National Population in 2010
Portion of National Populationwithin Zambezi Basin
Important Environmental Issues
752 614 sq km
577 900 (76.8%)
13 million
8 517 600 (65.52%)
• Copper mining
• Water and air pollution
• Deforestation and wildlife depletion
• Urbanization
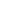
Z
AM
B
E
Z
I
R
I
V
E
R
BASIN L
I
M
I
T
Kasempa
Kaoma
Mumbwa
Kabwe
Kapiri Mposhi
Nyimba
Lundazi
Chipata
LUSAKA
Kafue
Mazabuka
Choma
Sesheke
Senanga
Mongu
Kalabo
Lukulu
Zambezi
Solwezi
Mwinilunga
Luanshya
Chingola
Chililabombwe
Mufulira
Ndola
Kitwe
Mansa
Mpika
Livingstone
DEMOCRATIC
REPUBLIC
OF CONGO
ANGOLA
ZIMBABWE
BOTSWANA
NAMIBIA
MOZAMBIQUE
MALAWI
TANZANIA
ZAMBIA
K
a
f
u
e
K
a
b
o
m
p
o
Lake
Bangweulu
Elevation
Metres above
sea-level
0
200
500
1 000
3 000
2 000
1 500