100
The United Republic of Tanzania, made up
of mainland Tanganyika and the islands of
Zanzibar, is surrounded by several large bodies
of water including 1 300 km of coastline on
the Indian Ocean and 2 375 km of shoreline
along Africa’s three largest lakes: Tanganyika,
Victoria, and Nyasa (UNEP 2008). The economy
is based on agriculture, which accounts for
more than half of GDP, provides 75 per cent of
exports, and employs about 75 per cent of the
workforce. The major limitation for cultivation
is topography and climate. Tourism is another
significant contributor to GDP, as is the
mining sector.
Progress towards environmental
sustainability
Reverse the loss of environmental resources
The three largest lakes in Africa by volume or
size – Lake Tanganyika, Lake Nyasa (Malawi/
Niassa) and Lake Victoria – cover 5.7 per cent
of Tanzania’s total surface area (UNEP 2008).
However, pollution from agriculture, industry,
mining, and households is threatening the
country’s water resources and untreated
industrial waste causes significant levels of
localized pollution. About 80 per cent of
the industries, including agro-chemical and
chemical industries, breweries and steel
manufacturing industries, are located in the
coastal area of Dar es Salaam and pollute
the Indian Ocean directly or indirectly
(UNEP 2008).
The proportion of land area covered by forests
has dropped by 19 per cent since 1990 due to
deforestation, leaving just over one-third of the
land under forests as shown in Figure 4.38. Much
of the fuelwood that is cut is converted to charcoal
for use in urban households. Rural industries also
use substantial amounts of fuelwood. Alternative
methods need to be applied and indigenous
knowledge systems should be incorporated into
sustainable harvesting.
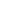
Tanzania
Total Area of Country
Portion of Country within Zambezi Basin
National Population in 2010
Portion of National Populationwithin Zambezi Basin
Important Environmental Issues
945 087 sq km
27 300 (2.9%)
42 million
1 646 400 (03.92%)
• Water pollution and aquatic ecosystems
• Land degradation and deforestation
• Threats to biodiversity and ecosystems
Z
A
M
B
E
Z
I
R
I
V
E
R B
A
S
I
N
Shinyanga
ZAMBIA
MOZAMBIQUE
KENYA
UGANDA
DEMOCRATIC
REPUBLIC
OF CONGO
TANZANIA
Kahama
Tabora
Sikonge
Itigi
Singida
Manyoni
Babati
Mbulu
Ngorongoro
Arusha
Moshi
Same
Korogwe
Dodoma
Mpwapwa
Kilosa
Morogoro
Kibaha
Bagamoyo
DAR ES SALAAM
Kibiti
Masasi
Lindi
Tunduru
Kakonko
Biharamulo
Geita
Mwanza
Bukoba
Nyahanga
Musoma
Mikumi
Mpanda
Karema
Kipili
Uvinza
Kigoma
Kanyato
Kasulu
Nzega
Oldeani
Mbeya
Sumbawanga
Ifakara
Iringa
Njombe
Tukuyu
Tunduma
Mtwara
Kilindoni
Tanga
Lake Victoria
Lake
Nyasa
Lake
Tanganyika
Lake
Manyara
Lake
Eyasi
Lake Natron
Lake
Rukwa
I
g
o
m
b
e
S
h
a
m
a
W
a
m
i
P
a
n
g
a
n
i
R
u
fi
j
i
Zanzibar