96
Namibia is situated at the southern edge of
the tropics and is the most arid country in
southern Africa receiving an average of only
258 mm of rain per year. Humidity is very low
and the average rainfall varies from almost
zero in the coastal desert to more than 600 mm
per year in the Caprivi Strip. Rainfall is highly
variable and droughts are common. With only
2.5 people per square kilometre it is among
the least populated countries in the world (FAO
2007, UNEP 2008).
Progress towards environmental
sustainability
Reverse the loss of environmental resources
The country’s abundant natural resources,
particularly fisheries and mining, are the
backbone of the national economy. The
majority of the population is dependent on the
land, especially for extensive cattle, goat and
sheep farming. About 3 000 sq km – less than
one per cent of all land – is cultivated each
year, mainly for maize, sorghum and millet.
However, the arid and semi-arid nature of
the country coupled with recurrent droughts
and flooding, especially in the northern rural
areas, makes it difficult for the large part of the
population which is dependent on subsistence
agriculture.
Water availability is the single greatest factor
limiting development in Namibia. Extreme
temporal variability and uneven spatial
distribution of water resources constrain
livelihoods, particularly for the 64 per cent
of the population who live in rural areas
(Government of Namibia 2008). Perennial
surface water resources are limited, located
primarily along the northern and southern
borders, but all of these sources suffer
from significant population pressure and
degradation.
Overgrazing is the largest threat to the
environment since cattle, which outnumber
people in Namibia, have surpassed the carrying
capacity of the land. Current evidence of
desertification includes declining ground
Namibia
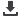
Total Area of Country
Portion of Country within Zambezi Basin
National Population in 2010
Portion of National Populationwithin Zambezi Basin
Important Environmental Issues
824 290 sq km
17 100 (2.1%)
2.1 million
70 350 (3.35%)
• Land degradation and desertification
• Aridity and water scarcity
• Biodiversity loss
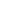
Elevation
Metres above
sea-level
0
200
500
1 000
3 000
2 000
1 500
Opuwo
Ongwediva
Tsumeb
Outjo
Swakopmund
Walvis Bay
Luderitz
Alexander Bay
Karasburg
Keetmanshoop
Bethanie
Maltahohe
Mariental
Rehoboth
Gobabis
WINDHOEK
Okahandja
Usakos
Karibib
Omaruru
Otjiwarongo
Otavi
Grootfontein
Katima
Mulilo
Cuangar
Rundu
Mucusso
A
u
o
b
O
r
a
n
g
e
C
u
b
a
n
g
o
Z
A
M
B
E
Z
I
R
I
V
E
R
B
A
S
I
N
L
I
M
I
T
SOUTH AFRICA
NAMIBIA
ZAMBIA
ANGOLA
BOTSWANA