4
Overview of the Zambezi
southeastern Angola and northern Zambia
onto a low-gradient area that forms the Barotse
floodplain. From the Ngonye Falls, the river
steepens, collecting water frommore tributaries,
including the Cuando-Chobe River that drains
southern Angola and Namibia’s Caprivi Strip.
Three hundred kilometres downstream, the river
drops a dramatic 100 metres forming the Victoria
Falls and marking the beginning of the river’s
middle section (Moore and others 2007).
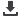
Figure 1.1
There are 63 transboundary river basins in Africa, covering 64 per cent of the continent’s land area (UNEP 2010). The Zambezi basin is the fourth
largest in Africa after the Congo, Nile and Niger River Basins (Mukosa and Mwiinga 2008).
The Zambezi River flows over a distance of
almost 3 000 kilometres, dropping in altitude
from its source in the Kalene Hills in the north-
western district of Solwezi in Zambia at 1 585
metres above sea level, to its delta in the Indian
Ocean, 200 kilometres north of the Mozambican
port of Beira (Chenje 2000).
The Zambezi River has tributaries along both
banks, and these drain portions of eastern and
SENEGAL
VOLTA
NIGER
CHAD
OGOOUE
CONGO
JUBA-SHABELLE
TURKANA
OKAVANGO
ORANGE
LIMPOPO
ZAMBEZI
NILE
AT L A N T I C O C E A N
Mediterranean
Sea
Red
Sea
I N D I A N O C E A N
Africa major river basins
Elevation
Main river basin
Zambesi river basin
Metres
0
200
-200
-1 000
-2 000
-3 000
-4 000
-5 000
-6 000
500
1 000
1 500
2 000
3 000
RICCARDO PRAVETTONI
GRID-ARENDAL 2011
Lake
Chad