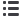
FIGURE 2. (A) Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) showed that human papillomavirus (HPV) status was the most important predictor of overall
survival. For HPV-positive tumors, the best outcomes were achieved in patients undergoing resection via the transoral approach with no perineural
invasion. For HPV-positive tumors resected with an open approach, margin status was a critical determinant of survival. In HPV-negative tumors,
extracapsular spread (ECS) was the next most important determinant of survival. Patients with HPV-negative tumors, ECS, and advanced T classifi-
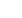
cation had the worst overall survival. (B) RPA allowed classification of patients into categories of low, intermediate, and high-risk of death. The
low-risk group comprised 41.9% of the entire cohort and the intermediate-risk group comprised 45.6% of the entire cohort, whereas the high-risk
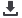
group represented 12.5% of the entire cohort. (C) Kaplan–Meier estimates of survival according to low, intermediate, and high-risk of death deter-
mined by RPA.
165