regardless of the index test result (item 6). Only 6 stud-
ies
15,20,24,26,33,36
made it clear whether or not clinical informa-
tion was available at the time of image interpretation (item
12). A graphical summary of the QUADAS assessment is pro-
vided (Supplementary Appendix 3 at
www.otojournal.org/ supplemental).
Diagnostic Accuracy of PET and PET/CT
Primary site.
For PET imaging of the primary site, there
were 18 studies with a total of 854 patients. The sensitivity
and specificity of FDG-PET or FDG-PET/CT in detecting
local residual disease or recurrences ranged from 50.0% to
100.0% and from 31.8% to 100.0%, respectively. The
Spearman correlation coefficient between the logit of sen-
sitivity and logit of 1-specificity was 0.298 (
P
= .230),
which suggested that a threshold effect was not present.
The pooled sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, and DOR
were 86.2% (95% CI: 79.8%-91.1%), 82.3% (95% CI:
79.3%-85.1%), 52.7% (95% CI: 46.4%-58.9%), 96.3%
(95% CI: 94.4%-97.7%), and 32.93 (95% CI: 19.17-56.56),
respectively (
Figure 2
). The area under the SROC curve
was 0.91 (standard error 0.02) with a Q
*
index of 0.85
(standard error 0.02), suggesting good diagnostic accuracy
(
Figure 3
).
Neck nodes.
For PET imaging of residual disease or recur-
rences in neck nodes, there were 15 studies involving 725
patients. The sensitivity ranged from 45.5% to 100.0%,
while the specificity ranged from 53.3% to 100.0%. The
pooled sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, and DOR were
72.3% (95% CI: 63.1%-80.4%), 88.3% (95% CI: 85.4%-
90.8%), 72.3% (95% CI: 63.1%-80.4%), 88.3% (95% CI:
85.4%-90.8%), and 22.84 (95% CI: 9.42-55.38;
Figure 4
),
with no correlation between sensitivity and 1-specificy
(Spearman correlation coefficient –0.359,
P
= .189). The
area under the SROC curve was 0.86 (standard error 0.04)
with a Q
*
index of 0.80 (standard error 0.03;
Figure 5
).
Distant metastases.
For PET imaging for the detection of
distant metastases at recurrence, there were 3 studies
involving 182 patients. The sensitivity and specificity
ranged from 69.2% to 100.0% and from 92.2% to 97.4%,
respectively. The pooled sensitivity, specificity, PPV,
NPV, and DOR were 84.6% (95% CI: 65.1%-95.6%),
94.9% (95% CI: 90.1%-97.8%), 84.6% (95% CI: 65.1%-
95.6%), 94.9% (95% CI: 90.1%-97.8%), and 81.47 (95%
CI: 21.6-307.31;
Figure 6
). The Spearman correlation
coefficient between logit of sensitivity and logit of 1-spe-
cificity was 0.5 (
P
= .67), suggesting an absence of
threshold effect. The area under the curve was 0.978
(standard error 0.02), with a Q
*
index of 0.93 (standard
error 0.04).
Multiple sites combined.
Some studies reported on the detec-
tion of residual/recurrent disease at all sites combined (ie,
local, nodal, and distant residual/recurrences considered
together). This included 9 studies with a total of 662
patients, of which 4 studies reported on data for local,
nodal, and/or distant recurrent disease separately as well as
together. For the detection of recurrent or residual disease at
any site, the sensitivity ranged from 53.8% to 100%, while
the specificity ranged from 47.7% to 95.5%. The pooled
sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, and DOR were 81.6%
(95% CI: 75.1%-87%), 86.3% (95% CI: 82.9%-89.3%),
81.6% (95% CI: 75.0%-87.0%), and 33.60 (95% CI: 16.16-
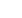
Citations identified using search strategy
(n = 3411)
Abstracts considered relevant and evaluated
(n = 312)
Full-text articles retrieved and assessed for
eligibility
(n = 150)
Abstracts rejected (n = 162):
•
review articles (n = 37)
•
conference proceedings (n = 30)
•
letters to editor (n = 3)
•
articles could not be obtained (n = 6)
•
lacked results of interest (eg initial staging of
disease rather evaluation of recurrent disease)
(n = 86)
Articles rejected (n = 123):
•
histological type not specified or included non-
SCCs (n = 51)
•
dual head gamma cameras in coincidence mode
used for image capture, (n = 5)
•
patients receiving surgery alone without
radiotherapy or chemotherapy (n = 29)
•
insufficient diagnostic accuracy data provided
for extraction (n = 9)
•
not prospective in design (n = 29)
Studies included in systematic review and
meta-analysis (n = 27)
Figure 1.
Literature flow diagram.
Cheung et al
26