In our systematic review and meta-analysis, we included
only prospective studies that used dedicated PET or PET/
CT scans for the detection of residual/recurrent disease in
patients with SCCs of the head and neck. Our review
included 27 prospective studies, comprising 1195 patients,
published between 1993 and 2014. There were 6 studies
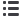
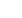
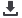
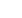
Figure 7.
Forest plots of sensitivity and specificity for positron emission tomography and positron emission tomography/computed tomo-
graphy in the diagnosis of residual and/or recurrent disease at multiple sites combined.
Table 2.
Summary Estimates of Sensitivity and Specificity and the Results of Subgroup Analysis for Imaging Modality, Image Analysis, and
Timing of Scan
Local Residual/Recurrent Disease
Nodal Residual/Recurrent Disease
Subgroup
Sensitivity, % (95% CI)
Specificity, % (95% CI)
Sensitivity, % (95% CI)
Specificity, % (95% CI)
Imaging modality
PET
90.7 (82.5-95.9)
76.5 (72.0-80.6)
a
72.0 (60.4-81.8)
87.7 (83.9-90.8)
PET/CT
80.8 (69.9-89.1)
89.8 (85.8-92.9)
a
73.0 (55.9-86.2)
89.4 (84.5-93.2)
Image analysis
Visual
86.7 (78.4-92.7)
80.2 (75.5-84.4)
63.9 (50.6-75.8)
88.4 (83.4-92.4)
Semiquantitative
85.2 (73.8-93.0)
84.2 (80.1-87.8)
81.8 (64.5-93.0)
88.6 (84.3-92.0)
Timing of scan
\
12 wk
84.8 (75.0-91.9)
79.9 (76.1-83.4)
b
67.5 (56.1-77.6)
86.2 (82.6-89.3)
c
.
12 wk
87.5 (77.6-94.1)
88.4 (83.0-92.6)
b
82.6 (61.2-95.0)
96.0 (90.1-98.9)
c
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; CT, computed tomography; PET, positron emission tomography.
a
Statistically significant difference (
P
\
.001).
b
Statistically significant difference (
P
= .009).
c
Statistically significant difference (
P
= .004).
Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery 154(3)
29