Ten-Year Network Development Plan 2017 Main Report |
249
7.4.2 POWER TO GAS
Power to gas (P2G) is the name for technology and process that converts electrical
power into a gaseous energy. Through this process, the excess production of renew-
able electricity which would normally be curtailed can be used to produce hydrogen
by electrolysis. This technology is considered an important element in turning sys-
tem and sector coupling into a reality
1)
.
This could offer a solution to the challenges of balancing electricity production and
consumption, especially in a world of increased intermittent renewable generation,
and offers a highly flexible means of renewable energy storage. Although using this
hydrogen to generate electricity involves further efficiency losses, there are other
uses which avoid this, such as the use of hydrogen as fuel for transport.
P2G does not only offer the possibility to store renewable energy but also to trans-
port it over long distances by using the gas transmission network, saving costs to the
European energy system by utilising the existing infrastructure.
As Hydrogen changes the quality of natural gas and has an impact on the heating
value, there are currently doubts and restrictions on the hydrogen percentage that
can be injected into the gas grids. However, there has been intense research
2)
aim-
ing at defining optimum injection rates and identifying measures to make current
gas infrastructure fit for hydrogen. On top of this, there is the option to combine the
hydrogen in a second step with CO ² by a methanation process, producing synthetic
methane that can be injected easily into the natural gas grids, and used in any gas
application e. g. as heating energy in modern hybrid systems or as a fuel for trans-
port.
As CO ² is also retained from other sources, the synthetic methane is carbon neutral.
P2G as a green energy storage could make an important contribution to the energy
transition.
1)
http://etogas.com/fileadmin/documents/news/2015_Fraunhofer_ISE_Study_PtG.pdf2)
http://www.dbi-gruppe.de/hips-net.htmlFigure 7.2:
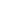
Example of P2G filling station installation (Berlin 2011) (Source: Enertag 2013)
Hydrogen generation
Hydrogen storage
Biogas storage
Mixing
valves
Wind energy plants
Power grid
combined heat
and power units
District
heating
Fuels
2010 2011 201
CURRENT
HYDROGEN
HYDROGEN
VARIABLE MIXING
BIOGAS
WARMTH
HYDROGEN
CURRENT
CURRENT