HAZARDOUS AREAS + SAFETY
‘non-issue’ items raised during the review, but not include these
items in the information incorporated into operator training and plant
operational manuals.
Case Study - Metal fluoride salts plant
A pilot scale facility was designed for the production of a transition
metal fluoride salt within the boundaries of a larger production
complex. When designed, the plant consisted of a raw material stor-
age area, a solution make-up area, the salt production area, product
handling area and final product storage. However the requiredmarket
for the metal fluoride salt product that the plant was designed for
was never secured, and the facility was subsequently mothballed.
Subsequent to the mothballing, some of the equipment installed on
this plant has been removed for utilisation in other processes in the
larger production complex.
This mothballed facility has been earmarked to be utilised for
metal fluoride salts production by BFluor (a different metal fluo-
ride salt than it was originally designed for). In order to utilise this
pilot plant for this product, the plant must be de-mothballed and
refurbished, as well as a redesign with relation to some portions of
the facility. Due to the deviation from the original design intent of
the process, several constraints are imposed by the current design
with relation to the new process. Significant retrofitting and process
modifications are therefore required to ensure that the facility is able
to meet the BFluor process’ intent.
Brief process description
Raw materials for the production of the metal fluoride salt include:
metal oxide, Anhydrous Hydrogen Fluoride (AHF), water and a base
solution. The metal oxide powder is stored in a storage hopper in
the raw materials storage area. The AHF is stored in a 100 m
3
tank
with 20% freeboard. The demineralised (‘demin’) water is supplied
from the water supply pipeline. The base is a powder (used to make
up the base solution) stored in a storage hopper.
The first stage of the process is the make-up of the solutions
required in the process, a 70% HF solution and a 20% base solution.
The HF dilution occurs in the HF dilution tank (a polypropylene tank)
while the base solution make-up is done in two separate make-up
tanks (polypropylene tanks).
The metal fluoride salt reaction occurs in two vessels. In the first,
the metal oxide powder is dissolved into the 70% HF to produce a
metal fluoride acid. This in turn is reacted with the base solution in
the next reaction vessel to form the metal fluoride salt. Subsequent
Abbreviations/Acronyms
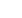
Figure 2: High level block flow diagram.
AHF
– Anhydrous Hydrogen Fluoride (AHF)
HAZOP – Hazard and Operability Study
HF
– Hydrogen Fluoride
IBC
– Intermediate Bulk Container
PFD
– Process Flow Diagram
P ID – Piping & Instrumentation Diagram
SIS
– Safety Instrumented System
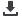
Figure 1: Typical HAZOP Methodology as adapted from IEC-61882.
21
March ‘16
Electricity+Control