How a complementary
waveform generator found in
8bit microcontrollers can help
in motor driver applications
A
complementary
waveform
generator (CWG) can be handy for
when half-bridge and full-bridge
control is needed, such as in motor
driver applications, for example.
Even better if the generator also has
selectable input sources, polarity
control, auto-shutdown and auto-
recovery.
These functions can be provided
as a peripheral in some 8bit
microcontrollers with no processor
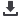
overhead. Fig. 1 shows a block
diagram of such a peripheral.
Each block in this diagram
represents a feature of the CWG,
which generates a complementary
output from one of several selectable
inputs. The output can be modified
in different modes of operation,
such as push-pull, half bridge, full
bridge and steering PWM.
The clock source can be selected
and used to insert a dead-band delay
between the pair of complementary
output waveforms. Each output pin
has individual output enable control
and the polarity of these pins can be
controlled individually. The output
can also be terminated immediately
during a fault and recovered when
the fault is removed.
Selections
Input sources can be external inputs
to the CWGxIN pin or outputs from
other internal peripherals. The input
source selection bits are used for
selecting the input source. The input
sources and bit selection settings
may vary from device to device.
Some of the available peripherals
that can be used as input sources are
the comparator, capture compare
PWM (CCP), numerically controlled
oscillator (NCC) and configurable
logic cell (CLC). First, though,
the selected peripheral should be
configured as the CWG’s input. For
devices that have peripheral pin
select (PPS), the CWGxIN input
pin can be moved to any other pin
with the PPS input selection register
(xxxPPS). By changing the “xxx”
notation in the register name to
CWGxIN, any available IO pin can
be selected as CWGxIN.
The CWG output can be modified
to operate in any of the following
modes: half bridge; forward full
bridge; reverse full bridge; push-
pull; and steering PWM. Mode
selection is only available in some
devices, where it can be selected by
setting the mode selection bits. For
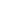
example, Fig. 2 shows the output
of the CWG in different modes
of operation for the Microchip
PIC16F161X family.
In half-bridge mode, two output
signals are generated as true and
Using a Complementary Waveform
Generator
Mike Gomez, Microchip Technology
18 l New-Tech Magazine Europe