magnetic field in the inductor. This
process is repeated continually.
At resonance, the series impedance
of the two elements is at a minimum
and the parallel impedance is at
maximum. Resonance is used for
tuning and filtering, because it
occurs at a particular frequency
for given values of inductance and
capacitance.
To cancel the influence of the
inductive reactance and the
capacitive reactance they should
have equal magnitude, ωL = 1/ωC,
so:
Where L is the inductance in
Henrys, C is the capacitance in
Farads , and ω = 2πf, in which f is
the resonance frequency in Hertz.
In low-power systems and for high
power efficiency, higher k and Q are
required.
Applications of inductive coupling
Taking inductive coupling a step
further, the idea of using it to
transmit power wirelessly has been
around since the mid 19th century.
Nikola Tesla initially experimented
successfully with the lighting of
gas-discharge lamps wirelessly over
a distance of approximately 15 feet.
This sparked interest in wireless
power transfer technology and
applications involving microwaves,
lasers, and solar cells capable of
transmitting power from space.
Closer to home, modern power
mats used to charge mobile devices
use resonant inductive coupling,
but use a "handshake" between the
charging surface and the device,
and then energy is transferred
to the device. It is an intelligent
system and will only send power to
identified devices and only at a rate
determined by the charging profile
of the device’s battery.
Inductive power transfer is also the
operating principle behind passive
RFID tags, toothbrushes, and
contactless smart cards.
Integrating wireless power and data
The principle challenges with
a contactless connector are
integrating the power coils and
near-field antenna into a very
small form factor that is relatively
easy to manufacture. This requires
knowledge of mechanical design
and power electronics, as well as
magnetics, RF circuit design and
antennas.
The power-transmit portion takes
the 24-V DC supply, puts it through
a circuit protection section, followed
by a DC-DC converter and a DC-AC
converter. The converter output
feeds the transmit primary coil,
which has a capacitor in parallel as
part of a resonant tank that allows it
handle variable loads and distance.
The receiver side also contains a
resonant tank. The received power
is rectified, put through a DC-DC
converter to deliver 24 V DC to the
point of load.
The inductive power link itself has
an efficiency of approximately 95%,
while the output power is always
12 W. The overall system efficiency
depends on the data link and includes
the losses on the board, e.g. through
the DC-DC conversion.
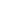
Figure 5. A contactless connectivity option implemented on a robotic arm allows 360 degrees
of freedom with no brush wear typical of current slip-ring designs. Integrated sensors also
enable “gentle touch” sensitivity. [Image courtesy of TE Connectivity]
Sensors
Special Edition
New-Tech Magazine Europe l 57