Technical article
January 2015
41
www.read-eurowire.comWater lubricating
application in wire and
coaxial cable drawing
process with nano-dies
By Zhang Wenhua, Guo Songshou, Zhang Zhiming and Shen Hesheng, Shanghai Jiaoyou Diamond Coating Co Ltd, and Shen Bin,
Sun Fanghong andWang Xinchang, Shanghai Jiaotong University, China
Abstract
An extremely effective new type of wire
drawing, cable compacting and tube
drawing die is capable of providing
dramatic benefits over PCD and tungsten
carbide dies in particular applications.
This paper introduces nanocrystalline
diamond composite coatings technology
applied to dies (nano-dies) and discusses
applications in aluminium wire drawing
and coaxial cable drawing. The benefits
of using nano-dies include significant
price/performance improvements, better
surface finish, higher productivity and a
most attractive green element – water
lubricating.
1 Introduction
There are many aluminium drawing
processes in the electric cable industry
and metal wire and tube industries,
including
aluminium
wire,
copper
clad aluminium wire (CCA), aluminium
enamelled wire, aluminium coaxial cable
and aluminium-plastics compound pipe.
Among these applications, one key factor
is preparation of a kind of drawing die
suitable for aluminium drawing, with high
production efficiency and product quality.
Conventional drawing dies for these
applications include tungsten carbide
(WC-Co) drawing dies (TC dies) and
several kinds of diamond drawings dies,
such as single-crystal diamond and
polycrystalline diamond (PCD) drawing
dies. Although diamond drawing dies
have the advantages of high hardness and
wear resistance, low friction coefficient
and good thermal conductivity, it remains
impossible
to
fabricate
traditional
diamond drawing dies with large bore
diameter at costs that would make
them easy or attractive to purchase.
Furthermore, these types of dies are easily
broken when drawing, especially at high
speed and for high strength material.
TC drawing dies can be manufactured
very economically in a wide range of bore
diameters (from 0.4 to 60mm or even
larger) and they are used in a wide range
of applications (due to their low cost), but
they also have serious disadvantages of
short working lifetime (easily worn and
lose tolerance quickly) and this translates
to low product quality and a huge
amount of wasted material, eg copper and
aluminium, which would be unacceptable
in mass production.
A solution to both of the problems has
appeared with the development of the
technique of chemical-vapour-deposited
(CVD) diamond films. Synthesis and
characterisation of diamond coatings have
gained wide spread research interests
[1]
and this wear-resistant coating can be
easily exploited for drawing dies. The
hot-filament CVD (HFCVD) diamond
coating on the interior hole surfaces of
WC-Co drawing dies provides particularly
good results, having the same advantages
as traditional diamond drawing dies, but
with higher performance in key areas.
For example, super high hardness
(70~100 GPa), very low friction coefficient
(~0.1), super high thermo-conductivity
(8~20W/cm
⋅
K) and chemical inertness.
Significantly, the HFCVD techniques
provide tremendous economic advant-
ages at larger bore diameters where
traditional diamond dies show relatively
weak economic performance. Specifically,
nano-dies enjoy spectacular success
replacing TC dies and PCD dies for copper
and aluminium power cable compacting
applications up to Ø60mm bore diameter
[2].
One of the key advantages of HFCVD
is production of diamond coatings
with low roughness. This has always
been a big challenge for conventional
multi-crystalline
diamond
surface
films. Because synthetic diamond films
deposited by conventional CVD processes
are multi-crystalline with a large grain size,
▲
▲
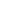
Figure 1
:
Illustration showing the appearance of the bias enhancement hot filament CVD fabricating apparatus for
nanocrystalline diamond composite coatings drawing dies
1 Filament
power source
2 DC source
3 Electrode holder
4 Reaction
gas inlet
5 Drawing die
6 Hot filament
7 Support
8 High
temperature
spring
9 Gas outlet