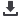
Figure 2: Traditional CPU/GPU approach compared with
Zynq-7000 / Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC
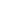
Figure 3: reVISION Stack
development of the application
which leverages the platform and
algorithm development layers.
Both the algorithm and application
levels of the stack are designed
to support both a traditional
image processing flow and a
machine learning flow. Within the
algorithm layer, there is support
provided for the development
of image processing algorithms
using the OpenCV library. This
includes the ability to accelerate
into the programmable logic a
significant number of OpenCV
functions (including the OpenVX
core subset). While to support
machine learning, the algorithm
development layer provides several
predefined hardware functions
which can be placed within the PL
to implement a machine learning
inference engine. These image
processing algorithms and machine
learning inference engines are
then accessed, and used by the
application development layer to
create the final application and
provide support for high level frame
works like OpenVX and Caffe.
The capability provided by the
reVISION stack provides all the
necessary elements to implement
the algorithms required for high
performance surveillance systems.
Accelerating OpenCV in
reVISION
One of the most exciting aspects
of the algorithm development
layer is the ability to accelerate a
wide range of OpenCV functions
within it. Within this layer, the
OpenCV functions capable of being
accelerated can be grouped into
one of four high level categories.
1. Computation – Includes functions
such as absolute difference
between two frames, pixel wise
operations (addition, subtraction
and multiplication), gradient and
integral operations.
2. Input Processing – Provides
support for bit depth conversions,
channel operations, histogram
equalisation, remapping and resizing.
3. Filtering - Provides support for
a wide range of filters including
Sobel, Custom Convolution and
Gaussian filters.
4. Other - Provides a wide range
of functions including Canny/Fast/
Harris edge detection, thresholding
and SVM and HoG classifiers.
These functions also form the
core functions of the OpenVX
subset, providing tight integration
with the application development
layer support for OpenVX. The
development team can use these
functions to create an algorithmic
pipeline within the programmable
logic. Being able to implement
functions in the logic in this
way significantly increases the
performance of the algorithm
implementation.
26 l New-Tech Magazine Europe