porting or redeveloping the entire
application may not be necessary, it
may even be possible to replace an
existing wire-based connection with
a wireless module with the minimum
of design effort.
A good solution in this case may
be the RN4020-V/RM120 Bluetooth
module from Microchip Technologies.
This module supports a number of
The module is based on an ARM
Cortex-M3 based microcontroller
and a Wi-Fi chipset, and as such
is able to run IoT applications in
a standalone mode. However, for
more complex applications, it is
also able to run alongside a host
(typically more powerful) processor,
interfacing through either a UART,
SPI or USB interface. In this mode,
the module is controlled by the host
using Silicon Lab’s high-level API,
written in C and intended to run on
the host processor alongside the IoT
application.
From W-LAN to PAN
While Wi-Fi is positioned to provide a
wireless alternative to Ethernet/LAN
connectivity, the technology behind
Personal Area Networks, or PANs, is
also making its way into the industrial
sector. Bluetooth, and now Bluetooth
4.0 (known as Bluetooth Smart or
Low Energy, also referred to simply
as BLE) provides a standard solution
for establishing peer-to-peer wireless
connectivity or ad hoc networks over
shorter distances. This is particularly
suitable for applications where
data is collected periodically using
a handheld terminal, for example.
The ENW-89847A1KF PAN1760 from
Panasonic is a BLE Smart Module
based on the TC35667 from Toshiba.
Measuring just 15.6mm by 8.7mm,
and 1.8mm high, it provides a pre-
certified solution to adding Bluetooth
connectivity to a new or existing
industrial application.
If wireless connectivity is being
fitted retrospectively to an existing
installation, as may be the case with
many industrial applications, then it
may be more advantageous to use
a dedicated module that can be
controlled using simple instructions
from an existing microcontroller
or processor. In this scenario,
Bluetooth services and is controlled
using simple ASCII-based commands
sent via the host processor.
Sub-GHz Solution
Operating in the 2.4GHz frequency
range of the ISM (Industrial,
Scientific and Medical) licence-
free band, modules based on both
Wi-Fi and Bluetooth offer simple
Figure 2: The WGM110A1MV1 Wizard Gecko
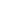
Figure 3: Block diagram of the ENW-89847A1KF PAN1760 from
Panasonic
62 l New-Tech Magazine Europe