Image 1:
Sentrius™ RG1xx
LoRa-Enabled Gateway from Laird
Image 2:
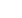
Communications in IoT network
LoRa is highly-scalable and
interoperable
LoRa technology is ideal for battery-
powered networks of IoT devices
because, like BLE, it is also an ultra-
low-power technology that can
operate for an extended time on a
battery and requires very infrequent
maintenance. The inexpensive nodes
allow companies to bypass the high
cost of cellular data fees or fiber/
copper installation to create the long-
distance data backhaul for remote
installations. Just as important is
LoRa’s ability to perform in harsh
environments, including industrial
settings where temperature, vibration
and interference are common. LoRa
is also highly-scalable and highly-
interoperable,
supporting
many
thousands of nodes and compatible
with both public and private networks
for the data backhaul and bi-directional
communications.
The primary limitation that LoRa has
involves data throughput, which makes
it a poor fit for high-data applications
that involve constant streaming of
information. But luckily, the vast majority
of EIoT sensor implementations simply
involve event data that are sent by the
networks back to a central location
and/or small-packet instructions sent
by managers to the networks in the
field. Those are small batches of data
rather than live streaming, making
LoRa an ideal technology to provide the
bi-directional communications.
LoRa+BLE complement
one another perfectly
* BLE connects small wireless
devices in any physical location
they are needed, creating an
integrated, short-range network
that can operate for a very long
time without battery changes and
be controlled from anywhere via
a smartphone or tablet. BLE also
can enable a wireless interface
to the sensor using the phone/
tablet screen in place of buttons
and switches, reducing the overall
cost / size of the sensors.
* And LoRa allows those BLE-
powered networks of devices to
go anywhere geographically by
providing an ultra-low power
means of communicating to
those IoT networks over a longer
distance.
Together, BLE and LoRa allow IoT to go
anywhere on the globe, making them
a critical technology pairing for driving
a new wave of IoT deployments that
don’t have geography as a limitation.
So what does an integration of LoRa
and BLE look like in action?
IoT
implementations
involving
temperature, light or proximity sensors
Most readers of EP&T Magazine have
likely done IoT implementations
involving temperature, light, or
proximity sensors that are connected
with BLE wireless technology. Those
types of sensor deployments are
very common in industrial settings
and for environmental monitoring,
so it is an example that should feel
very familiar to most readers. In this
application note, Laird engineers give
a detailed outline of how BLE and LoRa
collaborate in a typical temp sensor
project to enable these deployments to
go in dramatically different geographies
than previously possible.
The specs of the project will look very
familiar to most readers: a typical
board for the sensor, a temp sensor
that most readers have likely worked
with a dozen times before, etc. But by
using a LoRa+BLE module as the heart
of the deployment’s wireless strategy,
the network of sensors can rely on
the LoRa long-distance backhaul
for data transfer, all while operating
seamlessly with BLE for short-range
communication with each sensor.
The beauty of this example is that it
looks just like one of a dozen (or dozens
of) projects that each of you has worked
on in the past. Fundamentally, it is still
a BLE-based IoT deployment. But a
closer look makes it clear that this type
of implementation opens up doors that
were previously closed and locked and
boarded up as far as IoT was concerned.
LoRa breaks down those barriers, but it
does so without requiring engineers to
design in a radically different way.
This is just one example of how LoRa+BLE
can be used together. The true impact of
this pairing of technologies will come from
engineers revisiting all the times they
wished they could have deployed a BLE-
based network of devices in a location
but ran into the obstacle of unavailable
or too-costly wireless infrastructure.
Geography is no longer the limit. Now
the only limit is an engineer’s imagination
about how to put IoT to work.
Image 3:
900MHZ / 868 MHZ Module
With LoRa + Central Or Peripheral
BLE network
New-Tech Magazine Europe l 21