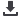
conductive, non-live exposed parts
e.g. housings. Additional protection
safeguards
against
dangerous
electrical shock and situations in
which basic and fault protections fails.
Fire protection uses RCDs to prevent
electrical fires caused by insulation
faults.
Types of RCDs
RCDs are characterised by the residual
current waveforms they can detect
and respond to, if they are dependent
or independent to the voltage, and
whether their trip response is instant
or delayed.
The ability to respond to various
current waveforms is important, and
the chosen RCD has to be suitable
for each waveform type. It is also
very important to note the different
tripping level for each waveform.
Several types of RCDs are available,
each for use with differing current
waveforms.
Type AC only detects sinusoidal
fault currents, but these are not
permitted in many EU countries.
Type A detects both sinusoidal and
pulsating DC residual currents. Type
F RCDs are primarily used for single
phase frequency inverter applications
to handle the residual currents with
frequency mixture up to 1kHz which
typically occur on the output of a single
phase frequency converter. They can
also detect sinusoidal AC currents as
well as pulsating DC currents.
Type B devices can detect sinusoidal
AC and pulsating DC as well as smooth
DC fault currents. RCDs of this type
are designed for use in three-phase
systems. Type Bfq comply with Type
B requirements while being designed
for use in circuits that include powerful
frequency converters for speed-
controlled drives. Type B+ have a
frequency tripping response defined
up to 20 kHz and provide superior
protection from fire risk caused by
ground fault currents in applications
with electronic drives.
In addition to the above, Type G, “Li”
and S RCDs have a trip delay and
hence a surge-withstand capability to
avoid nuisance tripping.
Classification of RCDs
RCD is the general term for all types
of residual current protective devices.
A standard residual current circuit
breaker is called an RCCB and some
further types of RCD exist; these are
described below.
RCD relays are devices with a separate
current transformer and contactor to
handle higher current ranges up to
400 A. However, RCD relays combined
with moulded case circuit breakers
(MCCB) offer a solution up to 1800A.
A residual current operated circuit
breaker with overcurrent protection
(RCBO) is a combination of an RCCB
with a miniature circuit breaker (MCB).
It provides overload, short circuit,
shock protection and fire prevention
from a single device.
Many different combinations can be
made from available RCD add-on
blocks and MCBs without having to
stock a large number of products.
This gives a high degree of application
flexibility and makes it easy to
customize the combination of RCD
and MCB devices.
RCD add-on blocks are also available for
MCCBs to cover applications up to 250A.
Digital RCDs
Digital RCDs combine protection
functionality with a set of digital
features, working together to provide
maximum circuit status information
and increase the protected system
or machine’s availability. The digital
technology is applied to both RCCBs
and RCBOs. Local pre-warning LEDs
and remote pre-warning potential-
free outputs can be provided in
the RCCB. These pre-warnings
allow maintenance staff to resolve
creeping problems before they lead
to interruptions or failures. Cost
savings accrue due to the reduction
in unscheduled service callouts and
further savings arise because test
intervals can be extended to once a
year only.
Sensors
Special Edition
Image 1:
Direct and indirect contact risks
New-Tech Magazine Europe l 59