well as drug infusion pumps. They
are also instrumental in continuous
positive airway pressure devices for
treating sleep apnea, and in negative
pressure wound therapy.
Non-invasive blood pressuremonitoring
is used to measure a patient’s systolic
and diastolic blood pressure via the
largely familiar inflating arm cuff.
Pressure is applied to the arm until
the artery is occluded, at which point
the blood stops flowing. Pressure is
released until blood starts flowing
(normally detected audibly), giving
the systolic pressure. As the cuff’s
pressure reduces the medical
professional will no longer be able
to detect audibly the flow of blood
in the artery; the diastolic pressure.
Using MEMS-based sensors, non-
invasive blood pressure monitoring
can be largely automated and it is
one of the biggest applications by
volume for MEMS pressure sensors.
Silicon Microstructures is a leader in
the design and manufacture of MEMS
pressure sensors and the SM4421 is
a good example of such a pressure
sensor used in this application. Housed
in a SOIC-16 package it integrates a
MEMS sensing element and signal
conditioning ASIC to provide a 14-
bit temperature-compensated output
through an I2C interface. Available in
gauge, differential and asymmetric
configurations, the devices that make
up SM4x21 series can operate across
a pressure range from 2.5PSI to
14.9PSI and can be used in a range
of different medical applications.
The Future of MEMS in the
Medical Sector
MEMS has the potential to transform
many aspects of medical care; the
concept of a lab-on-a-chip will lead to
fast and low cost diagnosis in remote
locations and developing countries
becoming a reality. The technologies
used to manufacture MEMS devices
are also employed in the development
of nanotechnology and the two are
closely related. This will see the
sciences of microfluidics further
merging with microelectronics, while
the introduction of new materials such
as carbon nanotubes and graphene
offers even greater potential.
Sensors
Special Edition
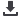
Figure 2:
The EVAL-ADXL362-ARDZ
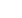
Figure 3:
A block diagram of the ICM-20948 9-axis MEMS motion tracking
multi chip module
New-Tech Magazine Europe l 57