Figure 1. Smart car systems
Figures 2-5).
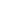
In this architecture, the power
management functions are added
to the on-board control PLD. The
control PLD monitors the "Power
Good" signals of the input supply and
each DC-DC converter (Fig.2). The
sequencing algorithm implemented
in a Control PLD generates the
sequence of "Enable" signals needed
to turn on the power to the payloads
without causing damage or logical
errors.
The Control PLD also generates
logical signals such as resets and
power good to ensure that the
payload devices can begin operation
during power up or terminate their
operations during power down. It
is also responsible for generating
a sequence to safely disable the
supplies during power-down or
when a fault is detected. PLDs can
easily support Event-Based solutions
which provide different responses to
different combinations of faults.
For this class of designs, all the
power sequencing, protection and
control functionality is implemented
within the Control PLD, typically
using VHDL or Verilog.
Pros:
•
Low cost
•
Straightforward architecture
enables
the
Control
PLD's
sequencing logic to be easily scaled
to accommodate new applications.
•
Designs can be implemented
using a single design environment
(typically VERILOG).
•
Event-based architecture can
respond to individual fault modes in
a flexible manner.
Cons:
•
Since each supply requires
two signal paths, larger, more
Power Architecture #1: Power Management &
Housekeeping by Control PLD
Fig.2: A Hardware Management system implemented using a
Control PLD to perform Power Management and Housekeeping.
Power Architecture #2: Power Management using Power
Manager ICs with Housekeeping by Control PLD
Fig.3: A Hardware Management system
implemented using Power Manager ICs and a
Control PLD.
28 l New-Tech Magazine Europe