Technical article
January 2014
78
www.read-eurowire.comThe heating rates were 5°C/min, 10°C/min,
15°C/min, and 20°C/min during these tests.
Figure 2
shows TGA test plots for optical
fibre samples made with single coat 200
μm OD of new and commercial coatings.
The results show better thermal stability of
the new coating in fibre format.
The weight loss results of fibre with the
new coating tested isothermally at 150,
180 and 200°C are shown in
Figure 3
.
The comparative plot of thermal stability
of 200-micron single coat fibre with new
and commercial coatings is shown in
Figure 4
.
Under isothermal heat aging at 150°C for
more than 1,000 hours, the new coating
again shows superior performance.
3 New coating
material fibre
sample tests
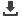
Attenuation temperature sensitivity was
measured for temperatures of 150°C,
180°C and 200°C.
Because
measurements
were
done
manually at room temperature after
particular exposure to elevated tem-
peratures, the measurement procedures
might contribute some ‘noise’ in the test
data.
Results of the attenuation test at 1550nm
wavelength for single mode fibres with
a single layer of new coating material at
several temperatures are shown in
Figure 5
.
Attenuation below 180°C is low and stable.
The experiment at 200°C will be continued
for more data.
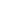
Fibre strength was measured by a tensile
tester at 500mm/min with a gauge length
of 0.5 metres.
The mean strength, the strength at 50%
failure probability in the Weibull plot, of
aged fibre samples is plotted in
Figure 6
.
It shows the new material single coat fibre
strength after temperature aging at 150°C
and 180°C. Fibre strength did not drop
after 1,000 hours of elevated temperature
exposure for all samples.
All of these results demonstrate good
long-term stability for temperatures below
180°C for optical fibres made with the
newly developed coating material.
4 Conclusions
A new mid-temperature acrylate type
coating material was developed. Optical
fibre samples made with a single coat layer
of the new material (coating diameter
of 200 μm) were tested in dynamic and
isothermal TGA tests demonstrating
superior performance in comparison with
the existing commercial mid-temperature
acrylate type coatings.
Long-term temperature aging tests in
normal atmosphere at temperatures up
to 200°C demonstrated stability of optical
fibre attenuation and fibre mechanical
strength.
n
The paper is courtesy of the 61
st
IWCS
International
Cable
and
Connectivity
Symposium, Providence, Rhode Island, USA,
November 2012.
5 References
[1]
E J Murphy, W W Cattron and J J Kelly, “Improved
Heat resistant UV Cure Compositions for Optical
Fibre Applications”, 57
th
IWCS Proceedings (2008)
[2]
D A Simoff, A A Stolov and C R Ciardiello,
“New Optical Fibre Coating Designed for High
Temperature Applications”, 58
th
IWCS Proceedings
(2009)
[3]
V A Kozlov and E J Murphy, “New UV Cure Heat
Resistant Coatings and Performance Durability of
Mid-Temp Optical Fibres”, 59
th
IWCS Proceedings
(2010)
[4]
B Overton and L White, “Aging Studies of High
Temperature Coatings”, 59
th
IWCS Proceedings
(2010)
▲
▲
Figure 6
:
Fibre strength test for newmaterial single coat optical fibre samples at 150°C and 180°C
Corning Incorporated
Corning
NewYork
USA
Tel
: +1 607 974 9227
:
kozlovva@corning.comWebsite
:
www.corning.com200 micron newmaterial fibre attn at 150°C, 180°C and 200°C
Mean strength, kpsi
Exposure time, hours