L’A
TLAS
DU
M
ONDE
DIPLOMATIQUE
I
19
civilian and military uses
International Atomic Energy Agency
(IAEA) there were only 24 nuclear
power stations under construction in
May 2005.
Some nuclear materials, in parti-
cular highly enriched plutonium and
uranium, may be used for civil purpo-
ses or in explosive devices. Attempts
to distinguish between civil and mili-
tary uses make increasingly little sense
technically and often provide an excuse
for disregarding measures to control
proliferation. In all the countries pos-
sessing nuclear weapons, progress
in civil nuclear science has benefited
arms development, and vice versa.
Although civil nuclear power plays a
relatively minor role in energy pro-
duction, the strategic potential of the
materials involved and the inherent
risk of amilitary or terrorist attack have
steadily increased. The stock of “civil”
plutonium exceeds 230 tonnes world-
wide and it is increasing. It represents
at least twice the amount contained in
the 30,000 nuclear warheads thought
to exist.
The Nuclear Non-Proliferation
Treaty calls on its signatories (China,
the US, France, the UK and Russia,
the acknowledged nuclear-weapon
states) to negotiate “general and com-
plete disarmament”. In practice they
have never stopped developing new
weapons. The US and Russia have
substantially reduced the number of
deployed warheads, but most of these
weapons were considered obsolete. A
genuine initiative for disarmament
would involve resumption of nego-
tiations for a treaty banning the pro-
duction of enriched plutonium and
uranium.
�������
������
�������
�������
����������������������������������������������������������
���������������������������
�������������������������������
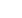
Eniwetok
Reggane
Hiroshima
Nagasaki
Mururoa
Christmas Island
Bikini
Aleutian
Islands
Nevada
Monte Bello
Islands
Novaja Zeml´a
Emu
Maralinga
Lop Nor
Kapustin
Yar
Say-Utes
Semei
(ex-Semipalatinsk)
PACIFIC
OCEAN
ATLANTIC
OCEAN
INDIAN
OCEAN
PACIFIC
OCEAN
Lira
Sources: International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), Vienna; Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, 2005; International Nuclear Safety Centre, 2002; Christian Bataille, Henri Revol, Les
incidences environnementales et sanitaires des essais nucléaires effectués par la France entre 1960 et 1996 et éléments de comparaison avec les essais des autres puissances nucléaires, French
National Assembly (report no 3571) and Senate (report no 207), Paris, 2002.
NB: figures for India, Israel and
Pakistan are estimates.
15 000
500
10 000
In tonnes (end of 2002)
80 40 10 2.5
Ackowledged nuclear-weapon states
Suspected nuclear-weapon states
Main nuclear explosions since 1945
The two sides to an industry
Serving the mining industry
>
Centre de documentation et
de recherche sur la paix et les conflits (CDRPC):
www.obsarm.org>
Federation of American Scientists (FAS):
www.fas.org/nuke/>
Arms Control Association (ACA):
www.armscontrol.org>
Power Reactor Information System (PRIS):
www.iaea.org/programmes/a2/>
Plutonium Investigation (WISE-Paris):
www.wise-paris.orgOn the web