EuroWire – March 2009
95
technical article
The feature that makes them interesting,
and worthy of increasing scientific
and technological excitement, rests in
fundamental length scales dominating
the morphology and properties of these
materials.
Between layered silicates the Mont-
morillonite
(Na+MMT)
avoids
to
obtain intercalated polymer. MMT is
environmentally
friendly,
naturally
abundant and economical. It has been
applied in numerous industrial fields due
to its good performance-cost ratio.
MMT
shows
di-octahedral
smectite
grouping, consisting of silicate layers of
approximately 200nm in length and 1nm
thick. The spacing between stacked layers
is approximately 1nm.
The outstanding feature of MMT is that
the silicate layers can be expanded
and even de-laminated by organic
molecules under proper conditions. Thus,
during the processing of polymer/MMT
nanocomposites, the nanoscale silicate
layers can be dispersed in the polymer
matrix and the reinforcement phase forms
in-situ on the molecular level, which is
very different from conventional filled
composites.
Moreover, it has been found that the polymer/
MMT nanocomposites can be prepared by
conventional processing techniques, such as
extrusion and injectionmethods.
4 Research and
development
B & B Compounds’ research activity
has focused on the preparation and
characterisation of:
nano-structured
material
with
•
Na+MMT
Sintetized Mineral Hydrozides (SMHs)
•
heavy metal free systems stabilisers
•
Ca-Zn
Tests were carried out using two basic
formulations of soft PVC used in sheathing
and insulation for electrical cables.
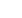
In the case of incorporation of Na+MMT
investigating the dispersion degree means
SEM (
Figure 1
) and XRD (
Figure 2
).
As can be seen in XRD and SEM, Na+MMT
is exfoliated. XRD pattern of Na+MMT
shows a peak of 2θ=7.2 but XRD pattern
PVC/Na+MMT
compound
decreases
intensity.
Several properties for cable applications
were investigated:
heat stability – CEI 20-34
•
LOI for flame retardance – CEI 20-22/4
•
accelerated ageing – CEI 20-34
•
HCl emission – CEI EN 50267-1
•
volume resistivity – ASTM D 257
•
smoke density – ASTM E 662
•
temperature Index – ISO 4589-3
•
Table
1
shows
that
PVC/Na+MMT
compound, though exfoliated, shows
some decreases in these properties.
In
Figure 3
the TGA (Thermo Gravimetric
Analysis) is reported as weight loss %/
temperature.
The first drop is the de-hydrochlorination.
The second drop between 425° and
600°C shows a loss of toluene and xylene,
formed from the polyolefin reticulated by
the temperature.
Further heating causes the formation of
aromatic polycyclic structures.
As show in
Figure 3
, at the first drop the
loss of volatile substances is CaZn.
Property
Units
Type of filler
Ca/Zn
Na+MMT
SMHs
Tensile strength
After 168h @ 100°
MPa
15
13
10
5
15
14
Elongation at break
after 168 h @ 100°
%
380
370
140
90
390
400
Heat stability
Minutes
60
10
100
LOI
%O
2
29*
25
29
HCl emission
mg/g
190
198
150
Volume resistivity
Ω.cm C° 20
0.06 X 10
14
0.01 X 10
14
1.2 X 10
14
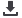
Note the size of the featured clay (Montmorillonite)
is 1mm thick and 100 – 500nm wide
Tetrahedral
sheet
Tetrahedral
sheet
Octahedral
sheet
Oxygen atom
Aluminium
Silicon
atom
C-axis
Table 1
▼
▼
*with Sb
2
O
3
MMT
▲
▲
Figure 1
▲
▲
:
SEM PVC/Na+MMT
Figure 2
▲
▲
:
XRD Na+MMT and PVC/Na+MMT
Figure 3
▲
▲
:
TGA SMHs compounds/CaZn compounds