177
and an uninterrupted connection between the city centre and the quarter Psie Pole
(North) and some western quarters of Wroclaw, which are highly affected by traffic
congestion during rush hours.
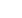
Figure 7.10 Green lines designate cycle lanes already built, red lines are suggested ones [5]
2. Wroclaw City Bike
On 8 June, 2011, Wroclaw City Bike was launched in the city in question. It is
a network of maintenance-free bike rentals operating within the so-called City Bike.
Initially, residents of Wroclaw had at their disposal 140 bicycles at 17 stations. In
April 2015, the system was expanded to 72 stations and 720 bicycles.
The first 20 minutes of the ride are free of charge. Subsequent minutes are paid.
The system is integrated with the Urban Card and credit card. The terminals are operated
in three languages – Polish, German and English. Every bicycle has its own lock, which
can be freely used for attaching the bicycle during use.
3. Park and Ride System
Developed cycling infrastructure and bike rental system are not the only aspects
of a successful cycle promotion strategy. A complex strategy consists of at least 6 points:
• Developed cycling infrastructure.
• Suitable height profile of the city.
• Bike-sharing system.
• Parking places for both bikes and cars with a good connection to the public
transport system.
• Restrictions for drivers – low emission zones, paid parking in the city – the
closer to the centre, the higher parking fees.
• Forcing of home-office could also reduce the kilometrage needed for one car.
In Wroclaw, there are not many places that are both easily accessible parking
places for cars and bikes. A good public transport availability should be obvious to make
sure that even non-cyclists have the option to leave the car in the city surroundings and
continue by public transport.