63
www.read-wca.comWire & Cable ASIA – January/February 2016
Material
Flame
retardant
Low
smoke
Halogen
free
PVC
X
–
No
Polyolefin
– –
X
Yes
Polyurethane
– –
X
?
TPE
–
X
?
FRNC
+
X
Yes
Fluorpolymer
+ +
No!
❍
❍
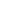
Table 2
:
Typical fire performance properties of cable compounds
The test purpose is to prove that no short circuit appears
when a defined burner flame works on the cable for the
required time. Fire resistance is more an aspect of impact
reduction.
3.3.4 Smoke Exhaustion
The quantity of smoke and fume is an important indicator.
Smoke reduces the sight of escaping people and rescue
teams, thus the translucence of smoke emissions is tested
according to IEC 61034. A high quantity of exhaustion as
well as very dense fumes reduces the light transfer. The
reduction of fire impacts is clearly the purpose of smoke
exhaustion parameters.
3.3.5 Absence of Halogens
There are different test methods described in IEC 60754:
to detect the acidity of smoke the quantity of halogen
carboxylic acid is determined (IEC 60754-1). The electrical
conductivity of smoke indicates the quantity of acid
radicals. This is to be tested according to IEC 60754-2.
Another test procedure in this standard is the toxicity of
smoke, measured by the pH value which indicates the acid
content of the smoke in a liquid solution.
All the tests and parameters to prove a cable to be halogen
free are aspects of impact reduction, too.
3.4 Cable Construction Aspects
In cable construction a lot of parameters affect the cable
fire performance. The selection of materials is of main
importance. Thus
Table 2
gives an overview for some
common compounds for cable insulation and jacketing
regarding the fire characteristics. This deals with the basic
material.
Of course compound engineering improves continuously
and by use of specific additives there are materials of the
same family available with far better fire performance.
Nevertheless we should remain realistic and keep in mind
that there will never be the perfect material. The addition
of mineralic fire retardants keeps the material halogen
free and reduces flame propagation, but it also reduces
mechanical properties such as elongation and elasticity.
But not only material affects the fire performance of
cables. A lot of detailed construction parameters are
important. So for example the tightness of a jacket should
be taken into account.
Interstice filling jackets provide more combustive material
to a fire, but they prevent the air flow inside the interstices
and reduce the oxygen available to the flame. A jacket
extruded as a tube has a similar effect as a funnel when
the cable is burning, especially in vertical fire tests.
4 Fire Protection Strategies
Fire protection is not only a cabling issue. There must be a
general fire protection concept regarding all construction
elements of a building. This need is taken into account in
the European Constructive Products Regulation
[6]
.
We have seen there are two aspects of fire protection:
fire avoidance and reduction of fire impacts. How do
these aspects correlate to the regional differences in fire
protection strategies?
4.1 Fire Avoidance
The common fire protection philosophy in America is to
prevent fire at any cost. There are high amounts invested
into research and investigation and the results are very
challenging regulations regarding the fire performance of
indoor cabling in terms of self ignition, flame propagation
and fire resistance.
To meet these requirements there is no other way than to
use halogens as flame retardants in cable compounds, as
well as in building materials.
This approach risks the threat of personal injury by acid
fumes and of emergency exits being hidden by dense
smoke.
4.2 Reduction of Fire Impacts
It seems to be complete nonsense to reduce potential
fire impact but to do nothing to avoid fire. And it really is,
because there are so many and various impacts of fire.
There may be very specific situations where
such a scenario makes sense, but such an exotic
application shall not be discussed in this paper.
Nevertheless we do not know any regulations which just
support this approach.
Reduction of fire impact cannot be a fire protection
strategy itself but it should be an important part of a
combined strategy, as it is European standard.
4.3 Diverse Redundancy
It is said that Europeans and especially Germans have a
preference for multiple safety. We are happy to know there
is a second protection instrument if the first protection
instrument should fail.
Combined safety strategy is well-known in many
technologies relevant to safety. So in safety discussions
regarding nuclear power plants the idea of diverse
redundancy is a basic approach.
This means there must be an additional safety procedure
which works completely independently from the first one in
case the basic safety procedure does not work.
So in Europe it is the consensus to avoid fire as much
as possible but at the same time to keep low the
consequences on health or goods if a fire happens.
Due to physical reasons a better reduction of the effects
is achieved by reduced fire avoidance. But in total the risk
according to
Equation (1)
is significantly lower. This is also
shown in
Figure 2
.