customers to plug-in their highly-
specialized proprietary technologies,
policies, and procedures. For
example, the hardware interconnect
design - such as inputs from tamper
detection sensors - can be COTS,
while programmed behavior (such as
in FPGAs) for tamper response can be
Commissioned. The Commissioned
behavior is never exposed since it is
not part the COTS design process, yet
the anti-tamper framework is tightly
coupled with the architecture.
Prevent, Detect,
Respond: The 3 Tenets of
Anti-Tamper
An attacker seeks to gain information
from a secure system. Attacks
can be passive or active in nature.
Passive attacks include side-channel
analysis to ascertain secrets from
timing, dynamic power consumption,
or electromagnetic leaks; as well
as probing circuits or imaging
joint effort with the Communications
Security Establishment (CSE) for the
Canadian government. Laboratory
testing qualifies modules to one
of four levels of security. FIPS140-
3 is a draft standard which aims to
incorporate additional concepts and
provide modified requirements and
limits within the four levels of security.
Going Global: Common
Criteria
The Common Criteria for Information
Technology Security Evaluation (CC),
or ISO/IEC 15408, is an international
standard for computer security
certification. It is a unification of
European, Canadian, and US DoD
standards. Profiles and functional
requirements drive design, and
laboratory testing results in an
Evaluation Assurance Level (EAL)
which indicates the robustness of
a security solution. The Common
Criteria Recognition Arrangement
(CCRA) provides for member countries
to mutually recognize evaluated
systems. CC is typically used for
firewalls and operating systems,
and does not specify cryptographic
implementation.
Anti-Tamper in the COTS
Domain
In-house design expertise and
relationships with key partners and
suppliers make it possible to offer
standard COTS products with optional
security features. However, it becomes
necessarytodrawadistinctionbetween
COTS capabilities and Commissioned
content - sensitive, restricted, or
classified customer-specific methods.
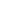
See Figure 1. The AT features
highlighted in yellow are the focus of
this paper. The COTS/Commissioned
dichotomy leverages lower-cost,
reliable COTS software, partitioning,
encryption, silicon features, and
physical materials, while allowing
New-Tech Magazine Europe l 41